Gypsy Language and Grammar- A Comparative Study with Indo-European Languages
Book Specification
| Item Code: | NAV547 |
| Author: | Vagish Shastri |
| Publisher: | Vagyoga Chetana Peetham, Varanasi |
| Language: | English |
| Edition: | 2004 |
| ISBN: | 8185570248 |
| Pages: | 322 |
| Cover: | PAPERBACK |
| Other Details | 7.00 X 5.00 inch |
| Weight | 300 gm |
Book Description
The Gypsies are a famous race which migrated from India between the 1' and 12' centuries, arriving in European countries during the 12' century AD. Before the Gypsies other peoples have made vast migrations in ancient times. The real name of the Gypsies, as used by themselves, is Roma (male) and Romni (female). Their native place from where they migrated was _famous in Puranic period as Rama Province near Punjab, Rajasthan and Sindh provinces. They became known as Gypsies because they entered European countries from Egypt.
When Gypsies migrated from India, their spoken language was Sanskrit mixed with Prakrit and ApabhraiiiSa. Gradually their language developed to the modern day and now resembles Hindi, Rajasthani and Punjabi languages.
Gypsies adopted different religions. Entering then Turkish Empire, they accepted Islam, and they adopted Christianity in the European countries. But they did not change their basic culture and language. They borrowed words from Persian, Turkish, Greek and other European languages. Somewhere they used semantical changes, such as the meaning of the Sanskrit word Trisala, trident. When they lived in Europe they did not see the trident. But there was an impression on their minds that Tri§ala had some religious significance. So when they adopted Christianity they used this word Trigala to mean cross.
This book consists of a deep etymological study of Gypsy vocabulary. Seventy five percent words of Romani language are related to Sanskrit, Prakrit, and Apabrarhia languages. The remaining other 25% words are connected to Persian, Turkish, Greek and European languages.. Somehow the spoken language is different from the literary language. The Sanskrit river was flowing in two different streams : literary and spoken. Now literary Sanskrit remains in India but the other varieties of spoken Sanskrit merged into later languages.
The Comparative study of Gypsy language with Indo-European languages will be of much interest to the curious readers as well as research scholars.
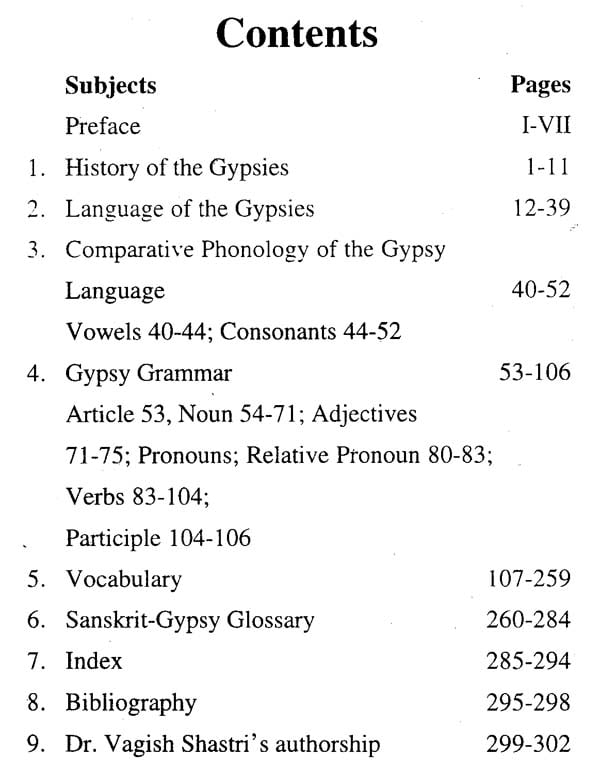
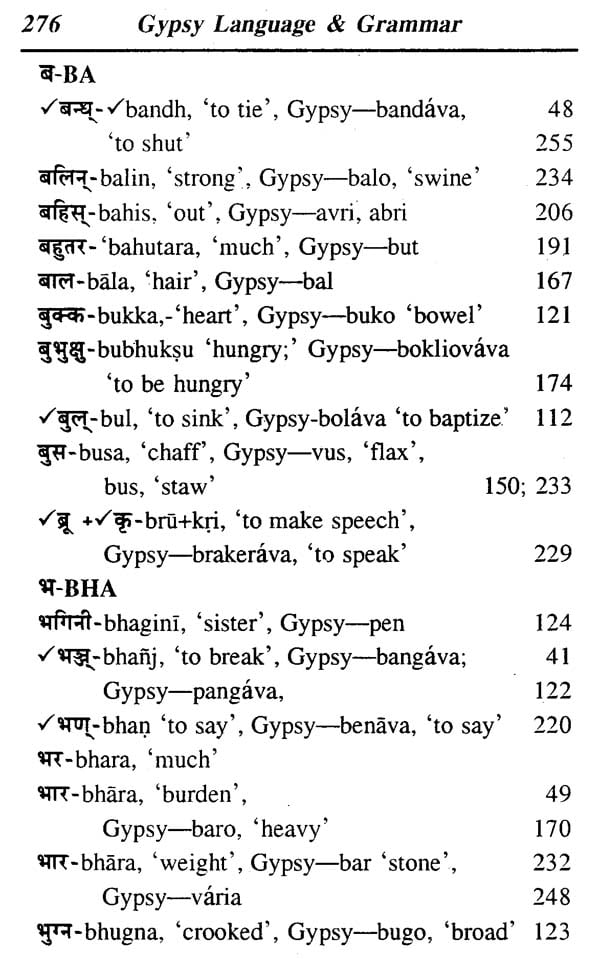
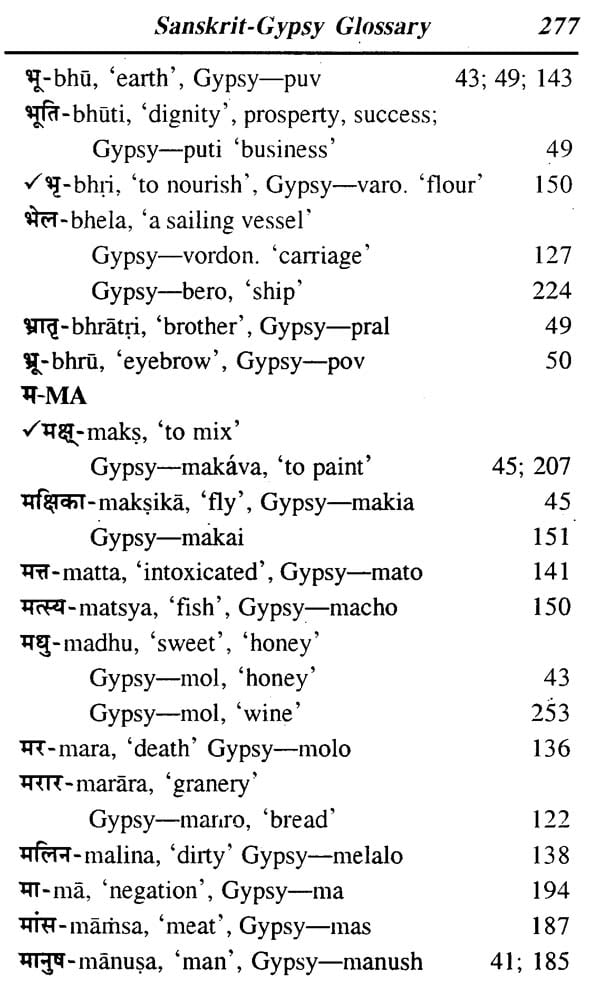
**Contents and Sample Pages**