Snakes
Book Specification
| Item Code: | NAJ055 |
| Author: | Neelimkumar Khaire |
| Publisher: | Jyotsna Prakashan |
| Language: | English |
| Edition: | 2013 |
| ISBN: | 9788179252307 |
| Pages: | 104 (Throughout Color Illustrations) |
| Cover: | Paperback |
| Other Details | 8.0 inch x 5.0 inch |
| Weight | 230 gm |
Book Description
Eminent herpetologist Neelimkumar Khaire has been closely associated with the study and conservation of snakes for over four decades. He is the Director of the ‘Snake Park’ and ‘Rehabilitation Centre for Animals’, Pune.
He is also the founder of the ‘Indian Herpetological Society’.
So far he has four publications about snakes and animals to his credit. All these books have been award-winning titles.
This new book ‘Snakes’ features 57 species of snakes found in India. Along with colour photographs and informative text, the book also covers important topics such as snake-bites, and first-aid measures for snake-bite victims. There are handy tables to help in the identification of snakes.
The simple, lucid text complemented by excellent photographs makes this book immensely helpful for farmers, trekkers, students of natural history and doctors alike.
‘Snake!’ the very word evokes feelings of horror and disgust in most of us. Snakes are also perceived as messengers of death. Like most people, I too harboured a fear of snakes, darkness and ghosts when I was a young man. The views of some of my seniors and other people around me only added to my fears.
For most of us life is following conventions and going down the well-trodden path. Same was the case with me and so in 1968, on my father’s advice, I took up a job in the Government tourism department. I was assigned my duty in Matheran as a Manager of the holiday home. At that time there were no proper roads. I made my way up to the hill station trekking through the forest. As I trudged along I dreamt about my future, and somewhere along the way I stopped to drink water.
Further on as I sought a place to rest, I got the shock of my life. The place I had chosen to rest was a small graveyard wherein lay the remains of seven Englishmen. Apparently they had all died of snake-bite under mysterious circumstances. The forest and the atmosphere around me affected me quite a bit. My enthusiasm vanished and was replaced by the fear of the unknown.
The thick forest of Matheran in those days not only harboured lots of snakes, but also was home to all kinds of wild animals. They all moved about freely. Everyday one would come across snakes at least three or four times. As for animals like civets, monkeys and birds, one just lost count.
I began working in Matheran, however my mind was in a turmoil. The monsoon was due soon. The tourist season becomes very lean during these rainy months. One spends most of the time doing repairs and maintenance work. It was while supervising such work that I encountered my first snake. I was apprehensive initially, but once I had caught it, fear gave way t curiosity. At that time, ideas about snake conservation and educating people about misconceptions about snakes had not even occurred to me.
I had just become very inquisitive about these mysterious creatures.
I gradually educated myself and learnt about the behaviour of snakes. I studied their role in the environment and their importance in the food chain. I realized that the inhibitions I had about them were incorrect. As I decided to find out more information regarding the biology of snakes for myself, the determination to observe their behaviour and other aspects of their life-cycle in the forest came naturally. My career in this new field had truly begun.
Initially, I was busy catching snakes and learning to identify them. However I had no teacher or a guide. There weren’t too many books on the subject. With a lot of effort, I obtained a book by Col. Gharpuray on snakes that was written in 1937. Shortly thereafter, I found a hundred year old publication –a Marathi book ‘Snakes of Hindusthan’, by VG Chiplonkar. Finally, I had some sources of information. My interest in snakes kept on growing and slowly it dawned on me that my life’s passion would be to study them.
The scientific study of snakes is called ‘Ophiology’. Nowadays many students are attracted to this discipline. Many of us now have realized that going against Nature is not sustainable and mankind can survive only if we consider ourselves a part of the eco-system and work in tandem.
Many species of snakes today are on the verge of extinction. During your lifetime some of them will even cease to exist. A large number of snakes are killed due to the misconceptions that we harbor about them. We must realize that snakes are a vital part of life on earth and are not expendable creatures.
Large tracts of forest that are home to innumerable snakes are being cleared for agriculture. To protect snakes we need to stop this deforestation. If something is not done about this, our future generations may see snakes only in photographs. So let us study them, get rid of our misconceptions, become their true friends and protect them.
This book deals with 57 species of snakes from amongst those found in our country. The photograph of the snake along with the English name, the scientific name, local names, its description along with its area of distribution, breeding behaviour, etc. have been provided.
In order to highlight the differences in similar looking snakes, their photographs have been presented side by side. For example, the File Snake (Acrochordus granulates) and the Hook-nosed Sea Snake (Enhydrina schistose) have been shown side by side.
Some of the information in this book is based on my personal observations and experience. Other books may have mentioned something different. There could even be some contradictory information. This is quite natural since snakes differ in their lengths as well as colouration, depending on local conditions and hereditary factors.
Another feature of this book is a comprehensive section on how to avoid snakes and snake-bites, signs and symptoms of poisoning, first-aid, newer methods of tying tourniquets and so on. I have also given charts that would help in identification of an unknown snake.
The coloured square at the top of the page indicates whether the snake is non-venomous (green square), semi-venomous (orange square) or venomous (red square).
(Special note: We have tried our best to give the local names of as many species as possible. In case anyone has additional information, do let us know so that we can include it in the next edition.)
| Introduction | 4 |
| About this book | 6 |
| Snakes | 10 |
| Snake anatomy | 13 |
| Brahminy Worm Snake (Non-venomous) | 22 |
| Beaked Worm Snake (Non-venomous) | 23 |
| Phipson’s Shieldtail (Non-venomous) | 24 |
| Mahableshwar Shieldtail (Non-venomous) | 25 |
| Indian Rock Python (Non-venomous) | 26 |
| Reticulated Python (Non-venomous) | 28 |
| Burmese Python (Non-venomous) | 29 |
| Common Sand Boa (Non-venomous) | 30 |
| Earth Boa/Red Sand Boa (Non-venomous) | 31 |
| Trinket Snake (Non-venomous) | 32 |
| Montane Trinket Snake (Non-venomous) | 33 |
| File Snake (Non-venomous) | 34 |
| Indian Rat Snake (Non-venomous) | 35 |
| Banded Racer (Non-venomous) | 36 |
| Slender Racer/Gunther’s Racer (Non-venomous) | 37 |
| Black-headed Royal Snake (Non-venomous) | 38 |
| Banded Kukri Snake (Non-venomous) | 39 |
| Russell’s Kukri Snake (Non-venomous) | 40 |
| Bronzeback Tree Snake (Non-venomous) | 41 |
| Common Wolf Snake (Non-venomous) | 42 |
| Barred Wolf Snake (Non-venomous) | 43 |
| Dumeril’s Black-headed Snake (Non-venomous) | 44 |
| Checkered Keelback Water Snake (Non-venomous) | 45 |
| Striped Keelback (Non-venomous) | 46 |
| Green Keelback/Grass Snake (Non-venomous) | 47 |
| Beddome’s Keelbak (Non-venomous) | 48 |
| Olive Keelback (Non-venomous) | 49 |
| Glossy-bellied Racer (Semi-venomous) | 50 |
| Dog-faced Water Snake (Semi-venomous) | 51 |
| Glossy Marsh Snake (Semi-venomous) | 52 |
| Ornate Flying Snake (Semi-venomous) | 53 |
| Common Indian Cat Snake (Semi-venomous) | 54 |
| Ceylon Cat Snake (Semi-venomous) | 55 |
| Beddome’s Cat Snake (Semi-venomous) | 56 |
| Forsten’s Cat Snake (Semi-venomous) | 57 |
| Condanarus Sand Snake (Semi-venomous) | 58 |
| Stout Sand Snake (Semi-venomous) | 59 |
| Leith’s Sand Snake (Semi-venomous) | 60 |
| Common Vine Snake (Semi-venomous) | 61 |
| Brown Vine Snake (Semi-venomous) | 62 |
| Indian Egg-Eater (Semi-venomous) | 63 |
| Banded Krait (Venomous) | 64 |
| Common Krait (Venomous) | 65 |
| Wall’s Sind Krait (Venomous) | 66 |
| Slender Coral Snake (Venomous) | 67 |
| Striped Coral Snake (Venomous) | 68 |
| Monocellate Cobra/Monocled Cobra (Venomous) | 69 |
| Spectacled Cobra/Indian Cobra (Venomous) | 70 |
| King Cobra (Venomous) | 72 |
| Hook-nosed Sea Snake (Venomous) | 74 |
| Many-toothed Sea Snake (Venomous) | 75 |
| Short Sea Snake (Venomous) | 76 |
| Russell’s Viper (Venomous) | 77 |
| Saw-scaled Viper (Venomous) | 78 |
| Hump-nosed Pit Viper (Venomous) | 79 |
| Malabar Pit Viper (Venomous) | 80 |
| Bamboo Pit Viper (Venomous) | 81 |
| Compare with | 50 |
| Glossy-bellied Racer (Semi-venomous) | 82 |
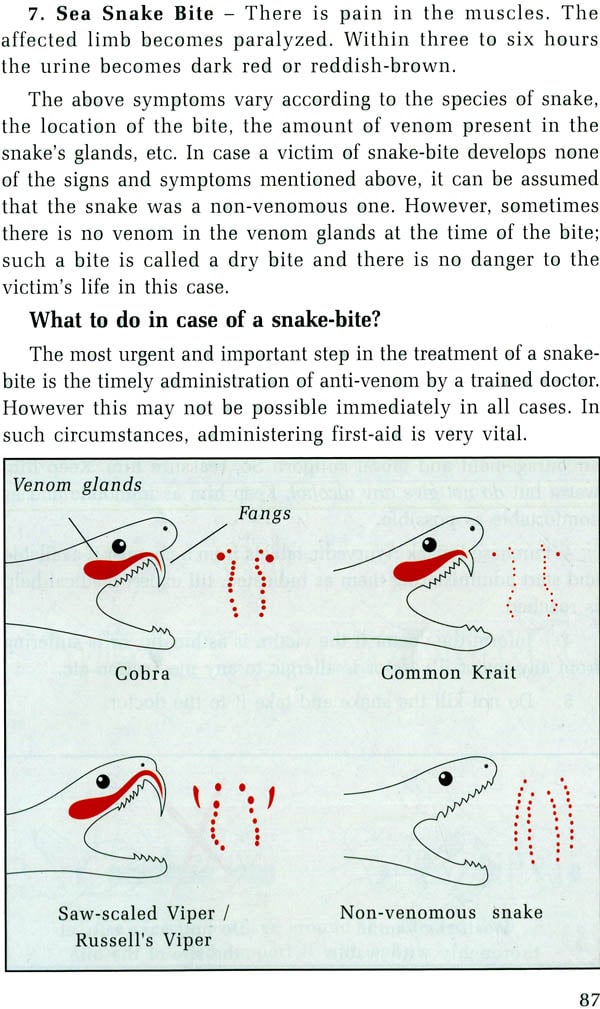
| Signs and Symptoms of a Venomous Snake-bite | 86 |
| First-aid | 88 |
| How to avoid snake-bites | 90 |
| What if a snake enters your house? | 93 |
| Common misconceptions about snakes | 94 |