All You Wanted To Know About Calories
Book Specification
| Item Code: | IDE635 |
| Author: | Pooja Malhotra |
| Publisher: | New Dawn Press |
| Language: | English |
| Edition: | 2010 |
| ISBN: | 9788120724648 |
| Pages: | 176 |
| Cover: | Paperback |
| Other Details | 6.0" X 4.5" |
| Weight | 140 gm |
Book Description
From the Jacket:
Healthy eating is healthy living. How true! But few amongst us rarely adhere to it as sip on the coke and dig in the pack of chips.
Guiding the calorie-conscious through weight management and nutritive value of food, this book weaves in several health tips and sumptuous recipes too.
A must-read for all those diet-watchers.
Most of us enjoy the food we eat - the variety of tastes that different cuisines have. However, food performs important functions in the body other than pampering our taste buds, and is essential for survival, growth, reproduction and for maintaining good health. As a popular saying goes, 'Don't live to eat, eat to live'.
Food is the 'fuel' which supplies chemical energy to our body to support daily activities and growth. Even fully grown adults require energy for survival, maintenance and repair of worn out tissues. The energy value of food is measured in heat units called calories.
Besides energy, food supplies our body with proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals and fibre. All these nutrients are required by our body in specific amounts. An imbalanced intake, that is, deficiency or excess, of any of these nutrients including energy, can impair health.
What is a calorie?
A calorie is a unit of measurement of energy. By definition, a calorie is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by 10 Celsius, specifically from 14.50 C to 15.50 C. The new unit of energy, which has been accepted by the International Union of Sciences and the International Union of Nutritional Sciences, is 'Joule'. One calorie is equal to 4.184 Joules (symbol 'J').
The kilocalorie, which is equal to 1000 calories, is the unit commonly used for measuring the amount- of energy which food provides. For all practical purposes, 'calorie' continues to be widely used for measuring energy content of foodstuffs and for estimating energy requirements of human beings. Kilocalorie will be referred to as calorie (symbol 'Cal' with 'C' in Capital), hereafter.
What calories do
Calories provide the fuel to keep the human body going. They provide our body with the energy that we require to perform all our body functions. We require energy for survival - to breathe, pump blood and for all kinds of physical activity like walking, running, sitting and working. Calories are required even when we are lying down or asleep. They are also expended in digestion of food, and for making available the calories from that food to our body. They are essential for maintenance of our body temperature. Thus, adults require calories mainly for physical activities and involuntary body functions. In case of infants and children in their growing years, besides the above mentioned roles, calories perform the very vital function of supporting growth and development.
| 1. | Introduction What is calorie? What calories do? | 5 |
| 2. | Your Caloric Needs | 10 |
| 3. | Food Sources of Calories Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Alcohol | 19 |
| 4. | Calorie Imbalance What is ideal body weight? Body fat Indices of weight status Overweight and obesity Health hazards of obesity Too much of anything makes you fat Underweight Health hazards of underweight | 48 |
| 5. | Weight Management: Obesity | 71 |
| 6. | Weight Management: Underweight | 98 |
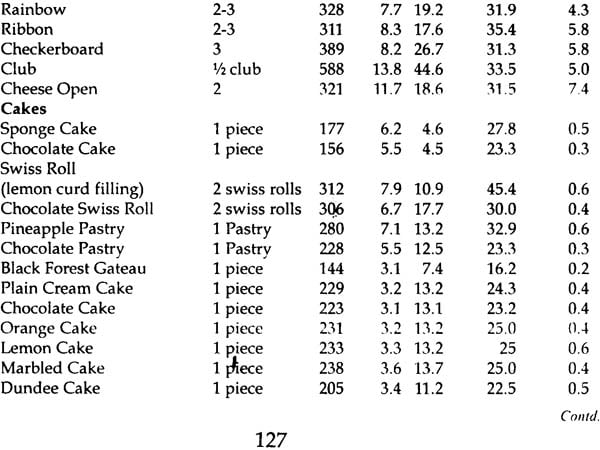
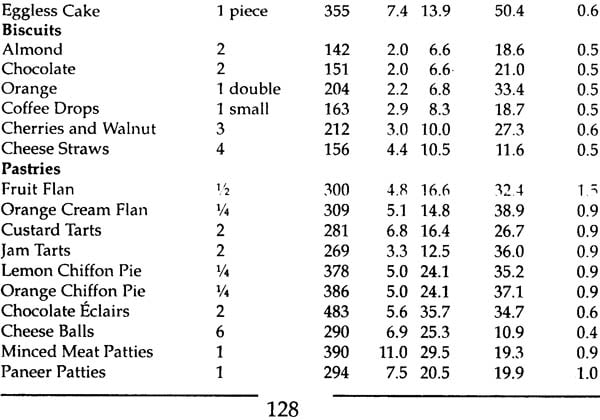
| 7. | Counting Calories Nutritive value of common ingredients Nutritive value of common recipes Energy expenditure in physical activity and sports | 103 |
| 8. | Tips for Controlling Calorie Intake Low calorie cooking methods Low calorie recipes Low calorie alternatives to high calorie foods Fibre - the wonder non-nutrient Artificial sweeteners Fat replacers | 134 |
| 9. | Nutrition - Myth and Facts | 166 |
| Appendix I- Recommended Dietary Allowances for Indians (ICMR) | 168 | |
| Glossary | 172 |