Caraka Samhita (Volume IV Cikitsa Sthan Chap. XV-XXVI)
Book Specification
| Item Code: | IDI547 |
| Author: | Dr. Ram Karan Sharma Vice-Chancellor K. S. D. Sanskrit University Darbhanga-Bihar and Vaidya Bhagwan Dash Deputy Adviser in Ayurveda Ministry of Health & Family Planning New Delhi |
| Publisher: | Chowkhamba Sanskrit Series Office |
| Language: | [Text With English Translation & Critical Exposition Based On Cakrapani Datta's Ayurveda Dipika] |
| Edition: | 2011 |
| ISBN: | 8170800153 |
| Pages: | 567 |
| Cover: | Hardcover |
| Other Details | 9.8" X 6.3 |
| Weight | 1 kg |
Book Description
From the Jacket
The Caraka Samhita stands at the top of the ancient texts representing the School of Medicine in Ayurveda founded by the great Scholar-Sage Punarvasu Atreya. Its value is further enhanced by the fact that it is the only text available in complete form where-as other contemporary Samhitas such as of Jatukarna, temporary Samhitas such as of Jatukarna, Parasara etc. perished, that of Bhela is incomplete and that of Harita is dragged into controversy. Thus any scholar desirous to know about the fundamentals of Ayurveda and its approach to life, health and disease has essentially to take resort to the study of this text unique in depth and divergence. It is rightly said, "whatever is not here can not be found anywhere else."
Historically too, it is quite interesting, Like an archaeological edifice. If it is dug into one would come across three distinct strate of authorship ascribed to Agnivesa, Caraka and Drdhabala in successive order.
And Translation This immensely valuable text needed since long a faithful and simple translation into English communicating the ideas as they are without divulging into dogmatic details which make the situation terse particularly for a young scholar. This comes from the pen of two erudite scholars of Ayurveda who has devoted the major part of the life in studying the text intensively from various angles and has command over both the languages concerned.
Thus the present work is a definite improvement in that its easy narrative style permits a Scholar not acquainted with Sanskrit syntax to grasp the various concepts of Ayurveda. Moreover, the present translation represents the first attempt of its kind to express in English the Ayurveda Dipika commentary by Cakrapanidatta, which sheds light after light on the text.
Vaidya Bhagwan Dash
Alongside what can be termed official medical science, the search for new drugs, and all the activity connected with the discovery of nature's secrets there exists a vast body of knowledge which stretches back into the ancient realms of time.
People without number throughout the world are fascinated by, and drawn to the world of alternative medicine which is receiving evermore recognition and appreciation in view of the use of the elements which our mother earth offers.
Vaidya Bhagwan Dash, former deputy adviser on Ayurveda to the Indian Ministry of Health, is a leading expert in a field which brings together ancient traditions and innovation in an attempt to meet the enormous needs of a country such as India.
On the sound basis of his medical training and research, Dash has furthered his studies, and as a recognised authority in Ayurveda has taken his knowledge and caring beyond his country.
He can look back on a long career in medicine and public service and among the many appointments he has held figures that of Director of the Yoga Research Institute in New Delhi.
The Pie Manzu Centre intends recognizing the contribution which Vaidya Bhagwan Dash has made to the health and well-being of mankind by awarding him the medal of the Presidency of the Italian Senate.
About the Author
Dr. Ram Karan Sharma (born March 20, 1927 at Shivapuri, Saran, Bihar) was initiated to Vedic and allied studies (including Ayurveda) on traditional lines by Pandit Ambikadatta Sharma at Lokamanya Brahmacaryasrama, Muzaffarpur. As a full bright scholar, he worked with Prof. M. B. Emeneau at the University of California, Berkeley, U. S. A. College Muzaffarpur and Dr. Ishvara Datta (Patna College) affiliated to Patna University.
He was founder Director, Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan; vice Chancellor, Sampurnanand and Sanskrit University and Kameshvara Singh Darbhanga Sanskrit University; Joint Educational Adviser, Govt. of India; Visiting of Bihar. Presently he is the President of International Association of Sanskrit Studies. Areas of his special interest are: Panini, Mahabharata, Darsana, Kavya and Ayurveda. More than one hundred research papers and about a dozen major publications he has authored. His creative writings include Sandhya (Poetry), a recipient of Sahitya Akademi award and Sima (Novel) a recipient of Bharatiya Bhasha Parishad award.
Vaidya Bhagwan Dash (born Oct. 1934 in Parbatipur, Orissa) has had an outstandingly brilliant academic career. In addition to graduate and postgraduate qualifications in Ayurveda, he holds a Master's degree in Sanskrit and a Doctorate from University of Delhi.
In the course of over forty years dedicated to research and practice of Ayurveda, Dr. Dash has attended several international conferences and seminars held in Brazil, Mexico, Italy and France. He was invited to deliver a course of lectures in Ayurveda at the Patrice Lumumba Friendship University, Moscow and the Australia School of Ayurveda at Adelaide, South Australia.
A Sanskrit scholar, he handles the English Language with equal felicity. A significant advantage to his propensity for research in Ayurveda is Dr. Dash's proficiency in Tibetan Medicine.
Author of over sixty important publications covering different aspects of Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine, he is recipient of several prestigious awards including a Gold Medal from the Presidency of Italian Senate for outstanding services he has made to the health and well-being of mankind.
He was deputy Adviser in Adviser in Ayurveda to the Government of India in the Ministry of Health and F. W. till 1981, when he took voluntary retirement to enable him to devote more time for academic and research activities. As a Consultant in Traditional Medicine of the World Health Organisation, he had paid several visits to Bangladesh, Bhutan, Burma and Mongolia to study and advise on the Health Development Programmes of those countries.
| | ||
| | ||
| | ||
| | ||
| Verse Paragraph Number | Page No. | |
| Introduction | 1-2 | 1 |
| Functions of Agni | 3-4 | 1 |
| Importance of Agni | 5 | 3 |
| Process of Digestion | 6-8 | 3 |
| Avastha-Paka | 9-11 | 5 |
| Bhutagni-Paka | 13 | 9 |
| Dhatvagni-Paka | 15 | 10 |
| Process of metabolic Transformation Nourishment of Upadhatus (Subsidiary Tissue Elements) | 17 | 14 |
| Malas (Waste-Products) | 18-20 | 15 |
| Prabhava or Specific Action | 20 | 16 |
| Time Taken for Metabolic Transformation | 21 | 17 |
| Answer to Query About Metabolic Transformation | 22-35 | 19 |
| Circulation of Rasa | 36-38 | 21 |
| Importance of Jatharagni | 38-41 | 22 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Ajirna | 42-44 | 24 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Ajirna in General | 45-46 | 25 |
| Signs of different Types of Ajirna | 47-49 | 26 |
| Irregular and sharp Agni | 50 | 27 |
| Normal State of Agni | 51 | 27 |
| Signs of Mandagni and Grahani-Gada | 51-54 | 28 |
| Premonitory Signs and Symptoms | 55 | 29 |
| Description of Grahani | 56-57 | 29 |
| Varieties of Grahani | 58 | 30 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Grahani | 59-64 | 30 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Grahani | 65-66 | 32 |
| Etiology, Sign and Symptoms of kahaja Grahani | 67-70 | 32 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Sannipatika Grahani | 72 | 33 |
| Description of Ama Grahani-Gada | 73-76 | 34 |
| Description of Nirama Grahani-Gada | 77-81 | 35 |
| Dasamuladya-Ghrta | 82-86 | 36 |
| Tryusanadya-Ghrta | 87 | 38 |
| Pancamuladya-Ghrta, [Taila] and Curna | 88-93 | |
| Determination of Sama and Nirama Types of Grahani-Roga | 94-95 | 40 |
| Citrakadya-Gutika | 96-97 | 41 |
| Pippalyadya-Curna | 106-107 | 44 |
| Maricadya-Curna | 108-110 | 44 |
| Yavagu | 112-114 | 45 |
| Diet and Drinks for Grahani | 115-117 | 46 |
| Butter-Milk | 117-120 | 46 |
| Takrarista | 120-121 | 47 |
| Elimination Therapy in Paittika Grahani | 122 | 48 |
| Diet for Paittika Grahani | 123-124 | 48 |
| Candanadya-Ghrta | 125-127 | 49 |
| Tiktaka-Ghrta | 128 | 50 |
| Nagaradya-Curna | 129-131 | 50 |
| Bhunimbadya-Curna | 132-133 | 51 |
| Supplement to Bhunimbadya-Curna | 134-136 | 51 |
| Kiratadya-Curna | 137-140 | 52 |
| Elimination Therapy for Kaphaja Grahani | 141 | 52 |
| Drinks for Kaphaja Grahani | 142-143 | 53 |
| Diet of Kaphaja Grahani | 144 | 53 |
| Butter-milk in Kaphaja Grahani | 145 | 53 |
| Madhukasava (First Recipe) | 146-149 | 54 |
| Duralabhasava | 152-155 | 55 |
| Mulasava | 156-159 | 56 |
| Pindasava | 160-162 | 57 |
| Madhvarista | 163-167 | 58 |
| Pippalyadya-Curna | 168-169 | 58 |
| Recipes | 170 | 59 |
| Ksara-Ghrta | 171-172 | 59 |
| Recipes | 173-176 | 60 |
| Bhallatakadya-Ksara | 177-178 | 60 |
| Duralabhadya-Ksara | 179-180 | 61 |
| Bhunimbadya-Ksara | 181 | 61 |
| Haridradya-Ksara | 182 | 62 |
| Ksara-Gutika | 183-185 | 62 |
| Fourth Recipe of Ksara | 186-187 | 63 |
| Fifth Recipe of Ksara | 188-194 | 63 |
| Treatment of Tridosaja Grahani | 194-196 | 64 |
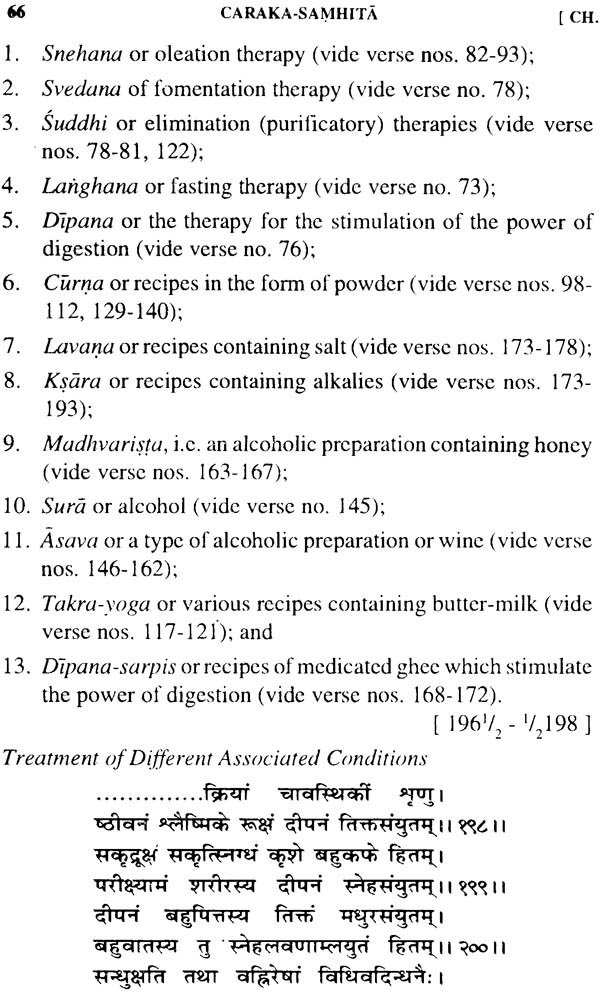
| Summary of Therapies | 196-198 | 65 |
| Treatment of Different Associated Conditions | 198-201 | 66 |
| Use of Fats | 201-205 | 67 |
| Treatment of Suppressed Agni | 206-211 | 69 |
| Food and Gastric Fire | 211-217 | 71 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Atyagni | 217-220 | 72 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Atyagni | 220-221 | 73 |
| Management of Atyagni | 221-235 | 73 |
| Different Types of Meal | 235-243 | 76 |
| Summary | 244-249 | 78 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 81 |
| Varieties of Pandu Roga | 3 | 81 |
| Pathogenesis in General | 4-6 | 82 |
| Etiology and Pathology | 7-12 | 83 |
| Premonitory Signs and Symptoms | 12 | 85 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Pandu in General | 13-16 | 85 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Pandu | 17-18 | 86 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Pandu | 19-22 | 86 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Kaphaja Pandu | 23-25 | 88 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Tridosaja Pandu | 26 | 89 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Mrd-bhaksanaja Pandu | 27-30 | 89 |
| Prognosis | 31-33 | 90 |
| Kamala (Jaundice) | 34-36 | 91 |
| Kumbha-Kamala | 37-39 | 92 |
| Line of Treatment : Pancakarma-Therapy | 39-43 | 93 |
| Dadimadya-Ghrta | 44-46 | 94 |
| Kutukadya-Ghrta | 47-49 | 95 |
| Pathya-Ghrta | 50 | 95 |
| Danti-Ghrta | 51 | 96 |
| Draksa-Ghrta | 52 | 96 |
| Haridradi-Ghrta | 53 | 97 |
| Two Recipes of Medicated Ghee | 54-55 | 97 |
| Purgation Therapy | 55-60 | 98 |
| Visaladi-Phanta | 60-63 | 99 |
| Recipes | 63-69 | 101 |
| Navayasa-Curna | 70-71 | 101 |
| Two Recipes of Mandurvataka | 72-77 | 101 |
| Tapyadi-Yoga | 78-80 | 102 |
| Yogaraja | 80-87 | 103 |
| Silajatu-Vataka | 87-93 | 104 |
| Punarnava-Mandura | 93-96 | 105 |
| Dravyadi-Leha | 97 | 106 |
| Mandura-Vataka (Another Recipe) | 102-105 | 107 |
| Gaudarista | 105-106 | 108 |
| Bijakarista | 106-111 | 108 |
| Dhatryarista | 111-114 | 109 |
| Drinks | 114-115 | 110 |
| Line of Treatment in General | 115-117 | 110 |
| Treatment of Mrd-Bhaksanaja-Pandu | 117-118 | 111 |
| Vyosadya-Ghrta | 119-121 | 111 |
| Recipe for causing Aversion for Mud | 121-123 | 111 |
| Line of Treatment of Mrd-Bhaksanaja-Pandu | 123-124 | 112 |
| Sakhasrita-Kamala | 124-128 | 112 |
| Food for Sakhasrita-Kamala | 128-130 | 113 |
| Duration of the Treatment | 130-132 | 114 |
| Halimaka Type of Jaundice | 132-134 | 114 |
| Treatment of Halimaka | 134-138 | 115 |
| Summary | 138-139 | 116 |
| | ||
| TREATMENT OF HIKKA AND SVASA (HICCUP AND ASTHMA) | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 117 |
| Serious Nature of Hikka and Svasa-Roga | 3-7 | 117 |
| Pathogenesis of Hikka and Svasa | 8-9 | 118 |
| Varieties and Etiology of Hikka and Svasa | 10-16 | 119 |
| Pathogenesis of Hikka and Svasa | 17-18 | 121 |
| Premonitory Signs of Hiccup and Asthma | 18-20 | 121 |
| Specific Pathogenesis of Hikka | 21 | 122 |
| Specific Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Maha-Hikka | 22-26 | 122 |
| Gambhira-Hikka | 27-30 | 123 |
| Vyapeta-Hikka | 31-33 | 124 |
| Ksudra-Hikka (Minor Hikka) | 34-37 | 125 |
| Annaja-Hikka | 38-41 | 126 |
| Yamika-Hikka | 42-44 | 127 |
| Pathogenesis of Svasa (Asthma) | 45 | 128 |
| Maha-Svasa | 46-48 | 128 |
| Urdhva-Svasa | 49-51 | 129 |
| Chinna-Svasa | 52-54 | 130 |
| Tamaka-Svasa | 55-62 | 131 |
| Pratamaka and Santamaka-Svasa | 63-64 | 133 |
| Ksudra-Svasa | 65-68 | 134 |
| Prognosis | 68-69 | 134 |
| Line of Treatment | 70-76 | 135 |
| Smoking-Therapy (Dhuma) | 77-80 | 137 |
| Treatment of Complications | 81 | 138 |
| Patients Unsuitable for Fomentation Therapy | 82-139 | |
| Alternate Fomentation Therapy for Unsuitable Patients | 83-84 | 139 |
| Management of Complications | 85-87 | 140 |
| Management of Four Different Conditions of Patients | 88-90 | 141 |
| Contra-indications of Elimination Therapy | 91-93 | 141 |
| Soups for Hiccup and Asthma | 94-100 | 142 |
| Diet and Yavagu for Hiccup and Asthma | 100-104 | 143 |
| Drinks for Hiccup and Asthma | 105-116 | 144 |
| Recipes of Linctus for Hiccup and Asthma | 117-120 | 147 |
| Panca-Karma Therapy | 121-122 | 147 |
| Satyadi-Curna | 123-124 | 149 |
| Muktadya-Curna | 125-128 | 148 |
| Recipes for Inhalation-Therapy, etc. | 129-134 | 149 |
| Recipes for Hiccup | 135-136 | 150 |
| Regimens to Avert Attacks of Hiccup | 137 | 151 |
| Eschewing the Etiological Factors | 138 | 151 |
| Administration of Medicated Ghee | 139 | 151 |
| Dasamuladya-Ghrta | 140-141 | 151 |
| Tejovatyadi-Ghrta | 141-144 | 152 |
| Manahsiladi-Ghrta | 145-146 | 152 |
| Line of Treatment in General | 147-150 | 153 |
| Summary | 151 | 155 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 156 |
| Prologue | 3 | 156 |
| Varietis of Kasa | 5 | 157 |
| Premonitory Signs and Symptoms of Kasa | 5 | 157 |
| Pathogenesis | 6-8 | 157 |
| Causes of Variation in Pain, etc. | 9 | 154 |
| Etiology of Vatika Kasa | 10 | 158 |
| Etiology of Pattika Kasa | 14 | 159 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Kasa | 11-13 | 159 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Kasa | 15-16 | 160 |
| Etiology of Kaphaja Kasa | 17 | 160 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Ksataja Kasa | 21-23 | 162 |
| Etiology of Ksavaja Kasa | 24-25 | 163 |
| Signs, Symptoms and Prognosis of Ksayaja Kasa | 25-30 | 163 |
| Line of Management | 31 | 165 |
| Treatment of Vatika Kasa: Line of Treatment | 32-34 | 165 |
| Kantakari-Ghrta | 35 | 166 |
| Pippalyadi-Ghrta | 36-38 | 167 |
| Tryusanadya-Ghrta | 39-42 | 167 |
| Rasna-Ghrta | 43-46 | 168 |
| Vidangadi-Curna | 47-48 | 168 |
| Dvi-Ksaradi-Curna and Satyadi-Kalka | 48-49 | 169 |
| Duralabhadi-Leha | 50 | 169 |
| Vidangadi-Leha | 51 | 169 |
| Citrakadi-Leha | 52 | 170 |
| Agastya-Haritaki | 53-56 | 170 |
| Recipes for Vatika Kasa | 57-62 | 171 |
| Smoking-Therapy | 65-68 | 173 |
| Manahsiladi-Dhuma | 69-70 | 174 |
| Prapaundarikadi-Dhuma-Varti | 71-72 | 175 |
| Manahsiladi-Dhuma-Varti | 73-74 | 175 |
| Ingudi-tvagadi-Dhuma | 75 | 176 |
| Food Preparations for Vatika Kasa | 76-82 | 176 |
| Treatment of Paittika Kasa : Emetic Therapy | 83-84 | 177 |
| Purgation Therapy | 85-86 | 178 |
| Recipes of Linctus | 87-89 | 178 |
| Sarkaradi-Leha | 90 | 179 |
| Tvagadi-Leha | 92-93 | 179 |
| Pippalyadi-Leha | 94 | 180 |
| Management of Thick and Thin Kapha | 97 | 180 |
| Post-Prandial Drinks | 98 | 181 |
| Soup, etc. | 99 | 181 |
| Medicated Milk | 100 | 181 |
| Recipes of Medicated Milk and Guda | 101-105 | 181 |
| Recipe for Pittaja Kasa | 106-107 | 182 |
| Line of Treatment | 108-111 | 183 |
| Decoction etc. | 112-117 | 184 |
| Recipes of Linctus (Leha) | 118-122 | 185 |
| Dasamuladi-Ghrta | 123-124 | 186 |
| Kantakari-Ghrta | 125-128 | 186 |
| Kulatthadi-Ghrta | 129 | 187 |
| Smoking Therapy in Kaphaja Kasa | 130 | 187 |
| Management of Associated Complications | 131-133 | 187 |
| Treatment of Ksataja Kasa : Line of Treatment | 134 | 188 |
| Pippalyadi-Leha | 135-137 | 188 |
| Treatment of Associated Complications | 138-139 | 189 |
| Medicated Ghee | 140 | 189 |
| Meat-Soup, etc. | 141-143 | 190 |
| Smoking Therapy | 144-148 | 190 |
| Treatment of Ksayaja Kasa: Line of Treatment | 149-150 | 191 |
| Medicated Ghee for Mild Purgation | 151-152 | 192 |
| Recipe of Medicated Ghee | 153 | 192 |
| Medicated Ghee and Medicated Milk | 154 | 193 |
| Recipe for Anuvasana Type of Enema | 155 | 193 |
| Diet After Anuvasana Therapy | 156-157 | 193 |
| Dvi-Panca-muladi-Ghrta | 158-160 | 193 |
| Guducyadi-Ghrta | 161-162 | 194 |
| Recipes of Medicated Ghee | 163-167 | 195 |
| Haritaki-Leha | 168-169 | 196 |
| Recipes of Powders and Linctus | 170-173 | 196 |
| Padmakadi-Leha | 174-175 | 97 |
| Jivantyadi-Leha | 176-179 | 197 |
| Recipes | 180-185 | 198 |
| Smoking Therapy | 186 | 199 |
| Management of Kasa in General | 187-189 | 200 |
| Different Categories of Therapies | 190 | 200 |
| Summary | 191 | 201 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 202 |
| Prologue | 3 | 202 |
| Mythological Origin of Diarrhoea | 4 | 203 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Atisara | 5 | 204 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Atisara | 6 | 207 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Kaphaja Atisara | 7 | 208 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Sannipatika Atisara | 8 | 210 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Sannipatika Atisara | 9 | 212 |
| Line of Treatment | 10 | 214 |
| Exogenous (Mental) Diarrhoea | 11 | 215 |
| Management of Exogenous (Mental) Diarrhoea | 12-13 | 215 |
| Line of Treatment | 14-19 | 216 |
| Recipes of Pramathya | 20-22 | 218 |
| Diet and Drinks | 23-25 | 219 |
| Group of Drugs Useful in Diarrhoea | 26-29 | 220 |
| Management of Diarrhoea Associated with Griping Pain | 30-33 | 221 |
| Treatment of Pravahika | 34 | 221 |
| Treatment of Varcah-Ksaya (Scanty Formation of Stool) | 35-41 | 222 |
| Prolapse of Rectum | 42 | 223 |
| Cangeri-Ghrta and Cavyadi Ghrta | 43-44 | 223 |
| Anuvasana Type of Enema for Prolapsed Rectum | 45 | 224 |
| Management of strangulated Prolapsed Rectum | 46 | 225 |
| Use of Medicated Milk | 47-49 | 225 |
| Treatment of Paittika Atisara | 50 | 226 |
| Recipes for Paittika Atisara | 51-56 | 227 |
| Administration of Milk | 57-60 | 228 |
| Anuvasana Type of Medicated Enema | 61-62 | 229 |
| Piccha-Basti (Mucilaginous Enema) | 63-68 | 229 |
| Raktatisara (Haemorrhagic Diarrhoea) | 69-70 | 230 |
| Treatment of Haemorrhagic Diarrhoea | 77-79 | 232 |
| Recipes for Haemorrhagic Diarrhoea | 77-79 | 232 |
| Darvyadi-Ghrta | 80-81 | 233 |
| Hemostatic Recipes | 82-86 | 233 |
| Treatment of anal Suppuration | 87-88 | 234 |
| Ointment for Anal Suppuration | 89-92 | 234 |
| Mucilaginous Enema for Griping Pain | 93-95 | 235 |
| Medicated Enema and Recipes of Linctus | 96-100 | 236 |
| Suppuration of Anal Sphincters | 101-102 | 237 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Atisara | 102-103 | 237 |
| Recipes for Kaphaja Atisara | 104-116 | 238 |
| Piccha-Basti and Anuvasana-Basti | 117-120 | 240 |
| Need for Immediate Treatment | 121 | 241 |
| Line of Treatment of Sannipatika Atisara | 122 | 241 |
| Summary | 123 | 242 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 243 |
| Prologue | 3 | 243 |
| Dialogue | 4-5 | 243 |
| Varieties of Chardi | 6 | 244 |
| Premonitary Signs and Symptoms of Chardi | 6 | 244 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Chardi | 7-9 | 245 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Chardi | 10-11 | 246 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Kaphaja Chardi | 12-13 | 246 |
| Chardi | 14-15 | 247 |
| Complications Leading to Incurability of Chardi | 16-17 | 248 |
| Dvistartha-Yogaja Chardi | 18 | 248 |
| Incurability of Chardi | 19 | 249 |
| Line of Treatment | 20-22 | 249 |
| Treatment of Vatika Chardi | 23-25 | 250 |
| Treatment of Paittika Chardi | 26-33 | 251 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Chardi | 34-39 | 253 |
| Treatment of Sannipatika Chardi | 40 | 255 |
| Treatment of Dvistartha Yogaja-Chardi | 41-44 | 255 |
| Treatment of Complications | 45 | 257 |
| Management of Chronic Chardi | 46-47 | 257 |
| Summary | 48 | 257 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 259 |
| Prologue | 3-10 | 259 |
| Name of the Ailment and Its Justification | 11 | 261 |
| Varieties of Visarpa | 12-14 | 261 |
| Seven Elements Involved in the Pathogenesis of Visarpa | 15 | 262 |
| Etiology of Visarpa in General | 16-22 | 262 |
| Location of Visarpa | 23-25 | 264 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Internal Visarpa | 26-27 | 265 |
| Characteristics of Incurable Visarpa | 28 | 265 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Vatika Visarpa | 29 | 265 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Visarpa | 30 | 266 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Paittika Visarpa | 31 | 267 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Visarpa | 32 | 267 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Kaphaja Visarpa | 33 | 269 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Kaphaja Visarpa | 34 | 269 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Agni-Visarpa | 35 | 270 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Agni-Visarpa | 36 | 271 |
| Etiology and Symptoms of Kardama-Visarpa | 38 | 272 |
| Etiology, Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Granthi-Visarpa | 39 | 274 |
| Complicatin (Upadrava) | 40 | 275 |
| Sannipatika Visarpa | 41 | 277 |
| Prognosis | 42 | 277 |
| Line of Treatment | 43-49 | 278 |
| Emetic Recipes | 51-53 | 280 |
| Decoctions | 54-61 | 280 |
| Recipes of Medicated Ghee | 62-68 | 282 |
| Blood-Letting Therapy for Peripheral Visarpa | 68-70 | 283 |
| External Therapies | 71 | 283 |
| Udumbaradi-Pradeha | 72 | 284 |
| Nyagrodhadya-Lepa | 73 | 284 |
| Kaliyadi-Pralepa | 74 | 284 |
| Sadvaladi-Pradeha | 75 | 284 |
| Sarivadya-Pralepa | 76 | 285 |
| Naladadya-Pralepai | 77 | 285 |
| Baladya-Lepa | 79 | 285 |
| Paste | 80-81 | 285 |
| Prapaundarikadya-Pralepa | 82-83 | 286 |
| Triphaladi-Pradeha | 87-88 | 287 |
| Khadiradyalepana | 88-89 | 287 |
| Recipes | 89-92 | 288 |
| Use of Ghee in Recipes | 92-93 | 288 |
| Recipes of Affusion | 94-95 | 289 |
| Durvadi-Ghrta and Darvyadyavacurnana | 95-96 | 289 |
| Recipe for Washing Ulcers | 97-98 | 289 |
| Method of Using Ointments (Pradeha or Lepa) | 98-107 | 290 |
| Wholesome Food and Drinks | 108-114 | 292 |
| Unwholesome Diet, Drinks and Regimens | 115 | 293 |
| General Line of Treatment | 116-117 | 294 |
| Treatment of Granthi-Visarpa | 118-120 | 294 |
| External Therapy for Granthi-Visarpa | 121 | 295 |
| Affusion for Granthi-Visarpa | 122-123 | 295 |
| Paste for External Application | 123-127 | 295 |
| Recipes for External Application Over Chronic Nodules | 127-131 | 296 |
| Cauterisation and Surgical Intervention | 132-136 | 297 |
| Treatment of Ulcers | 137-138 | 298 |
| Treatment of Galaganda (Goiter) | 139-140 | 299 |
| Importance of Blood-Letting Therapy | 141-143 | 299 |
| Summary | 144-146 | 300 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 302 |
| Prologue | 3 | 302 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Morbid Thirst in General | 4-7 | 307 |
| Premonitory Signs and Symptoms of Morbid Thirst | 8 | 304 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Morbid Thirst in General | 9-10 | 305 |
| Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Trsna | 11-12 | 306 |
| Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Trsna | 13-14 | 307 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Amaja Trsna | 15 | 307 |
| Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms of Ksayaja Trsna | 16 | 308 |
| Upasargaja Trsna (Morbid Thirst Manifested as complication) | 17 | 308 |
| Prognosis of Trsna | 18 | 309 |
| Important Role of Pitta and Vayu in the Pathogenesis of Thirst | 19-22 | 309 |
| Prohibition of Cold Water | 23 | 310 |
| Line of Treatment in General | 24 | 310 |
| Use of Rain-Water | 25-26 | 311 |
| Recipes of Medicated Drinks | 27-33 | 311 |
| Recipes and Regimens for Trsna | 34-39 | 313 |
| Treatment of Vatika Trsna | 40-41 | 314 |
| Treatment of Paittika Trsna | 41-46 | 315 |
| Treatment of Amaja Trsna | 47-49 | 316 |
| Treatment of Ksayaja Trsna | 50 | 317 |
| Utility of different Types of Water | 57-62 | 319 |
| Summary | 63 | 320 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 322 |
| Topics to be Discussed | 3 | 322 |
| Mythological Origin of Visa | 4-7 | 323 |
| Natural Aggravation and Alleviation of Visa | 3-7 | 323 |
| Jangama-Visa (Poison of Mobile Origin) | 9-10 | 324 |
| Sthavara-Visa (Poison of Immobile Origin) | 11-13 | 325 |
| Gara-Visa (Artificial Poisons) | 14 | 326 |
| Stages of Poisoning in Human Beings, Animals and Birds | 18-23 | 328 |
| Attributes of Poison | 24-27 | 330 |
| Variations in Symptoms Because of Dosas | 28-30 | 332 |
| Signs of Dusi-Visa (Artificial Poison) | 31 | 333 |
| The Cause of Death by Poison | 32 | 333 |
| Signs Indicating Death of the Poisoned Patient | 33-34 | 334 |
| Therapeutic Measures | 35-37 | 334 |
| Details of Therapeutic Measures (Arista, Utkartana, Nispidana & Cusana) | 38-39 | 336 |
| Blood-Letting, Etc. | 39-43 | 337 |
| Cheda (Excision), Etc. | 44-45 | 338 |
| Hrdayavarana (Protection of Heart), Etc. | 46-50 | 338 |
| Revival of an Apparently Dead Person | 51-53 | 340 |
| Mrta-Sanjivana-Agada | 54-60 | 341 |
| Treatment of Poisoning According to Location | 61-64 | 342 |
| Upadhana, Nasya and Anjana Therapies | 65-69 | 344 |
| Gandha-Hasti | 70-76 | 345 |
| Maha-Gandha-Hasti | 77-94 | 346 |
| Treatment of Complications Caused by Poisoning | 95-100 | 350 |
| Ksaragada | 101-104 | 351 |
| Examination of Attendants, Etc. | 105-106 | 352 |
| Signs of a Poison-Giver | 107 | 353 |
| Examination of Poisoned Food and Regimens | 108-111 | 353 |
| Signs of a Poison-Giver | 107 | 353 |
| Examination of Poisoned Food and Regimens | 108-111 | 353 |
| Other Characteristics of Poisoned Food, Drinks, Etc. | 112-123 | 354 |
| Animals Poisons | 123-129 | 356 |
| Identification of Sex and Breed of Biting Snakes | 130-135 | 358 |
| Virulence of Poison on the Basis of Age of Snakes | 136 | 359 |
| Colour of Fangs and Quantity of Poison | 137-139 | 359 |
| Insect Poison | 140-143 | 360 |
| Spider Poison | 144-146 | 361 |
| Rat Poison | 147-148 | 362 |
| Chamelion Poison | 149 | 362 |
| Scorpion Poison | 150-151 | 362 |
| Kanabha (Hornet) Poison | 152 | 363 |
| Uccitinga (Crab) Poison | 153 | 363 |
| Manduka (Toad) Poison | 154 | 363 |
| Poison of Fish and Leech | 155 | 363 |
| Poison of House-Lizard and Centiped | 156 | 364 |
| Masquito Poison | 157 | 364 |
| Maksika (Bee or Fly) Poison | 158 | 364 |
| Place, Time and Nature of Poison-Transmission Leading to Incurability | 159-161 | 365 |
| Augmentation and diminution of Poisoning Effects | 162-164 | 365 |
| Nature (Vatika, etc.,) of Poisons and Their Characteristic Signs | 165-169 | 366 |
| Line of Treatment | 165-169 | 366 |
| Poison of Rabid Dog and Other Wild Animals | 175-176 | 368 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Poisonious and Non-Poisonous Bites | 177-178 | 369 |
| Treatment of Poisoning | 179-188 | 369 |
| Recipes to Cure Snake-Poison | 189-199 | 371 |
| Recipes for Poisons of Insects, Etc. | 199-211 | 373 |
| Remedy Par Excellence | 212-214 | 375 |
| Recipe for Centiped-Poison | 215 | 375 |
| Recipe for House-Lizard Poison | 216 | 376 |
| Recipes for All Poisons | 217 | 376 |
| Panca-Sirisa Agada | 218 | 377 |
| Recipe for Poisons of Nails and Teeth | 219-220 | 377 |
| Sanka-Visa (Fear-Poison) and Its Management | 221-223 | 378 |
| Diet and Regimens | 224-228 | 378 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Poison in Quadrupeds | 229-230 | 379 |
| Signs, Symptoms and Treatment of Gara Type of Poison | 233-242 | 380 |
| Amrta-Ghrta | 242-249 | 382 |
| Thus It is Said | 250-253 | 383 |
| Summary | 254 | 384 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 385 |
| Appropriate Procedure of Taking Alcohol | 11-20 | 387 |
| Regimens to be Followed by Persons of Different Constitutions | 21-25 | 389 |
| Useful and Harmful Effects of Alcohol | 26-28 | 390 |
| Attributes of Alcohol Visa Vis Ojas | 29-36 | 390 |
| Specific Nature of Alcohol Prepared of Cereals | 38 | 393 |
| Effects of Excessive Intake of Alcohol | 39-40 | 393 |
| First Stage of Alcoholic Intoxication | 41-43 | 394 |
| Second Stage of Alcoholic Intoxication | 44-45 | 394 |
| Third Stage of Alcoholic Intoxication | 46-51 | 395 |
| Adverse Effects of Alcohol | 52-57 | 396 |
| Food Value of Alcohol | 58-60 | 397 |
| Effects of Alcohol Taken in Appropriate Manner | 61 | 398 |
| In Praise of Alcohol Taken Appropriately | 62-67 | 398 |
| Appropriateness of Alcohol Intake | 68-73 | 400 |
| Effects of Alcohol in Sattvika, Rajasika and tamasika Faculties | 74-78 | 402 |
| Friends to be Associated While Drinking Alcohol | 79 | 403 |
| Characteristics of Good Friends for Company During Alcohol Intake | 80-82 | 404 |
| Good Environment for Drinking Alcohol | 83-84 | 404 |
| Persons who do not get Intoxicated Easily | 85 | 405 |
| Persons who get Intoxicated Easily | 86-87 | 405 |
| Etiology, Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Madatyaya (Alcoholism) | 95-97 | 407 |
| Sannipatika Nature of All types of Madatyaya (Alcoholism) | 98-100 | 407 |
| Sings and Symptoms of Madatyaya (Alcoholism) in General | 101-106 | 408 |
| Line of Treatment | 107-111 | 409 |
| Justification of Giving Alcohol in Alcoholism | 112-116 | 411 |
| Pathogenesis and Treatment of Vatika Alcoholism | 117-120 | 412 |
| Recipe for Vatika Alcoholism | 121-122 | 212 |
| Meat Soup for Vatika Alcoholism | 123-124 | 413 |
| Vesavara and Pan-Cakes for Vatika Alcoholism | 125-126 | 413 |
| Meat and Pastries for Vatika Alcoholism | 127-128 | 414 |
| Post-Prandial Drinks for Vatika Alcoholism | 129-130 | 414 |
| Effects of Therapies | 131 | 414 |
| Other Regimens for Vatika Alcoholism | 132-135 | 415 |
| Drinks for Paittika Alcoholism | 136-137 | 415 |
| Food for Paittika Alcoholism | 138 | 416 |
| Soups for Paittika Alcoholism | 139-140 | 416 |
| Emetic Therapy for Paittika Alcoholism | 141-142 | 416 |
| Samsarjana-Krama | 143 | 417 |
| Treatment of Complications | 144-145 | 417 |
| Treatment of Morbid Thirst | 146-148 | 417 |
| Method of Giving Alcohol | 148-149 | 418 |
| Recipes of Morbid Thirst | 149-150 | 418 |
| Pancamlaka-Yoga | 151 | 418 |
| External Therapy for Paittika Alcoholism | 152-164 | 419 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Alcoholism | 164-169 | 421 |
| Food and Drinks for Kaphaja Alcoholism | 170-176 | 422 |
| Astanga-Lavana | 177-179 | 423 |
| Recipes of Digestive Stimulants | 180-184 | 424 |
| Other Regimens for Kaphaja Alcoholism | 185-188 | 425 |
| Treatment of Sannipatika Alcoholism | 189-190 | 425 |
| Regimens for Alcoholism | 191-193 | 427 |
| Psycho-therapy for Alcoholism | 194 | 427 |
| Milk for Alcoholism | 195-198 | 428 |
| Dhvamsaka and Viksaya | 199-205 | 429 |
| Virtues of Abstinance from Alcohol | 206 | 430 |
| Summary | 207-211 | 430 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 433 |
| Prologue | 3-4 | 433 |
| Preceptor's Reply | 5-6 | 434 |
| Exogenous and Endogenous Ulcers | 6-8 | 434 |
| Pathogenesis of Endogenous Ulcers | 10 | 436 |
| Treatment of Vatika Ulcer | 12 | 436 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Paittika Ulcer | 13 | 437 |
| Treatment of Paittika Ulcer | 14 | 437 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Kaphaja Ulcer | 15 | 437 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Ulcer | 16 | 437 |
| Characteristic Features | 17-19 | 438 |
| Twenty Varieties of Ulcers | 20-21 | 439 |
| Methods of Examination | 22-23 | 440 |
| Characteristic Features of Ulcer in Advanced Stage | 24-25 | 441 |
| Seats of Manifestation of Ulcers | 26 | 442 |
| Different Odour of Ulcers | 27 | 442 |
| Nature of Discharge From Ulcers | 28-29 | 443 |
| Complications of Ulcers | 29-31 | 444 |
| Impediments in Healing of Ulcers | 31-34 | 444 |
| Reasons of Ulcers becoming Difficult of Cure | 35 | 445 |
| Curable, Difficult of Cure and Incurable Ulcers | 36-37 | 446 |
| Sodhana or Elimination Therapy | 38-39 | 447 |
| Therapeutic Measure | 39-43 | 447 |
| Sopaghna (Therapeutic Measure to Relieve Oedema) | 44-48 | 449 |
| Surgical Interventions | 49-54 | 450 |
| Six Surgical Measures | 55 | 452 |
| Patana (Incision) | 56 | 452 |
| Vyadhana (Puncturing) | 57 | 452 |
| Chedana (Excision) | 58 | 453 |
| Lekhana (Scraping) | 59 | 453 |
| Pracchana (Scarification) | 59-60 | 453 |
| Sivana (Suturing) | 60-61 | 454 |
| Avapidana (Compression) | 61-62 | 454 |
| Nirvapana (Sprinkling Therapy) | 63-65 | 454 |
| Mamsa-Sandhana (Restoration of Muscle Tissue) | 65-68 | 455 |
| Asthi-Sandhana (Restoration of Fractured Bones) | 68-72 | 456 |
| Svedana (Fomentation) | 74-79 | 457 |
| Samana (Alleviation Therapy) | 74-79 | 457 |
| Esana (Probing) | 80-82 | 458 |
| Sodhana (Cleansing) | 83-85 | 458 |
| Ropana (Healing) | 86-94 | 459 |
| Patra (Application of Leaves Overs Ulcer) | 95 | 460 |
| Chadana (Padding) | 96 | 460 |
| Bandha (Bandage) | 96 | 461 |
| Bhojya (Diet and Regimens) | 97-98 | 461 |
| Utsadana (Elevation) | 99 | 461 |
| Avasadana (Removal of Excessive Granulation) | 100 | 462 |
| Agni-Karma (Cauterization including Heat) | 101-106 | 462 |
| Ksara (Application of Alkalies) | 107 | 463 |
| Dhupana (Fumigation Therapy) | 108-109 | 464 |
| Alepa (Application of Ointments) | 110-113 | 464 |
| Avacurnana (Dusting) | 113 | 465 |
| Ropana (Promotion of Healthy Skin) | 114 | 465 |
| Varnya (Restoration of Normal Skin Colour) | 115-117 | 465 |
| Loma-Rohana (Restoration of Growth of Hair) | 118 | 466 |
| Treatment of Complications | 119 | 466 |
| Summary | 120-121 | 466 |
| | ||
| | ||
| Introduction | 1-2 | 468 |
| Prologue | 3-4 | 468 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Udavarta | 5-6 | 469 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Udavarta | 6-10 | 469 |
| Line of Treatment of Udavarta | 11 | 470 |
| Vartti (Suppository) | 12-14 | 471 |
| Pradhamana (Insuffation) | 14-15 | 472 |
| Niruha Type of Medicated Enema | 16-17 | 472 |
| Diet for Udavarta | 18 | 473 |
| Purgation, and Anuvasana Type of Enema | 19 | 473 |
| Dviruttara-Hingvadi-Curna | 20 | 473 |
| Vacadi-Curna | 21 | 474 |
| Hingvadi Curna | 22 | 474 |
| Sthiradi-Ghrta | 23-474 | |
| Recipe | 24-25 | 475 |
| Emetic Therapy for Anaha | 26 | 475 |
| Use of Castor Oil | 27-31 | 476 |
| Etilogy of Mutra-Krcchra Dysuria | 32 | 477 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Dysuria Caused by Vayu, Etc. | 34-35 | 478 |
| Dysuria Caused by Urinary Calculus (Asmari) Pathogenesis | 36 | 479 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Urinary Calculus | 37-39 | 479 |
| Dysuria Caused by Sarkara (Graveluria) | 39 | 480 |
| Dysuria Caused by Semen | 40-41 | 480 |
| Dysuria Caused by Vitiated Semen | 42-43 | 480 |
| Dysuria Caused by Ksata (Vitiated Blood) | 43-44 | 481 |
| Treatment of Vatika Dysuria | 45-48 | 482 |
| Treatment of Paittika Dysuria | 49-51 | 483 |
| Recipes for Paittika Dysuria | 52-53 | 484 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Dysuria | 54-57 | 484 |
| Treatment of Sannipatika Dysuria | 58 | 485 |
| Treatment of Dysuria Caused by Calculus and Gravel | 59-68 | 486 |
| Treatment of Dysuria Caused by Vitiated Semen | 69-72 | 488 |
| Prohibitions in Dysuria | 76 | |
| Etiology of Heat-Diseases | 77 | 491 |
| Ailments Associated with Heart-disease | 78 | 491 |
| Specific Features of Different Types of Hrd-Roga | 79-80 | 492 |
| Treatment of Vatika Heart-Disease | 81-89 | 493 |
| Treatment of Paitttika Type of Heart-Disease | 90-95 | 495 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Type of Heart-Disease | 96-99 | 496 |
| Treatment Sannipatika Heart-Disease | 100 | 437 |
| Treatment of Angina in Sannipatika Heart-Disease | 101-103 | 497 |
| Treatment of Krmija Heart-Disease | 103 | 498 |
| Etiology and Pathogenesis of Pratisyaya (Rhinitis) | 104-105 | 499 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Vatika Rhinitis | 105 | 500 |
| Sings and Symptoms of Paittika Rhinitis | 106 | 500 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Kaphaja Rhinitis | 106 | 500 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Sannipatika Rhinitis | 107 | 501 |
| Dusta-Pratisyaya (Pernicious Rhinitis) | 107-109 | 501 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Dusta-Pratisyaya (Pernicious Rhinitis) | 110 | 501 |
| Pathogenesis of Ksavathu (Sneezing) | 11 | 502 |
| Pathogenesis of Nasa-Sosa (Dryness of Nasal Mucous Membrane) | 11 | 502 |
| Pathogenesis of Pratinaha (Nasal Obstruction) | 112 | 502 |
| Pathogenesis of Parisrava (Nasal Discharge) | 112 | 502 |
| Pathogenesis of Puti-Nasya (Ozena) | 113 | 502 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Apinasa (Chronic Rhinitis) | 113-114 | 503 |
| Nasa-Paka (Suppurative Rhinitis) | 115 | 503 |
| Nasa-Sotha (Oedematous Rhinitis) | 115 | 503 |
| Nasa-Arbuda (Nasal Tumour) | 116 | 503 |
| Puya-Rakta (Purulent and Sanguinous Rhinitis) | 116 | 503 |
| Arumsi (Furunculosis) | 117 | 504 |
| Nasa-Dipta (Burnt Nose) | 117 | 504 |
| Diagnosis of Siro-Roga (Diseases of Head) | 118 | 504 |
| Diagnosis of Mouth-Diseases | 119-123 | 505 |
| Etiology, signs and Symptoms of Arocaka | 124-126 | 506 |
| Signs and Symptoms of Ear-Diseases | 127-128 | 507 |
| Pathogenesis of Baldness and Premature Graying of Hair | 132 | 509 |
| Treatment of Vatika Rhinitis | 134-143 | 510 |
| Treatment of Paittika Rhinitis | 144-148 | 513 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Rhinitis | 149-156 | 514 |
| Treatment of Pernicious Rhinitis, etc. | 157 | 516 |
| Treatment of Head Diseases | 158 | 516 |
| Upanaha (Hot Poultices) | 159 | 516 |
| Rasnadi-Taila | 160 | 517 |
| Baladya-Taila | 161-162 | 517 |
| Mayura-Ghrta | 163-165 | 517 |
| Maha-Mayura-Ghrta | 166-174 | 519 |
| Ghee Prepared of Rat, etc. | 175 | 520 |
| Treatment of Paittika Headache | 176-179 | 521 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Headache | 180-182 | 521 |
| Treatment of Sannipatika Headache | 183 | 522 |
| Treatment of Krimija Headache | 183-186 | 522 |
| Line of Treatment | 187-188 | 523 |
| Pappalyadi-Curna | 188-190 | 524 |
| Tejovatyadi Tooth-Powder | 190-191 | 524 |
| Ksara-Gutika | 192-194 | 524 |
| Kalaka-Curna | 194-196 | 525 |
| Pitaka-Curna | 196-198 | 525 |
| Mrdvikadi-Curna | 198-200 | 526 |
| Katukadi-Kvatha | 201 | 527 |
| Darvi-Rasakriya | 202 | 527 |
| Administration of Ghee | 203 | 527 |
| Venesection, etc., in Stomatitis | 204-205 | 527 |
| Khadiradi-Gutika and Khadiradi-Taila | 206-214 | 528 |
| Line of Treatment of Anorexia | 215 | 529 |
| Kavala-Graha for Different Types of Anorexia | 216-218 | 530 |
| Karavyadi-Yoga | 219 | 530 |
| Panca-Karma Therapy, Etc. | 220 | 531 |
| Line of Treatment of Ear-Diseases | 221-222 | 531 |
| Hingvadi-Taila | 222-223 | 531 |
| Devadarvadi-Taila | 223-224 | 532 |
| Gandha-Taila | 224-225 | 532 |
| Ksara-Taila | 226-229 | 532 |
| Treatment of Diseases of Mouth, etc., in General | 230 | 533 |
| Line of Treatment | 231 | 533 |
| Bidalaka for Vatika Eye-Diseases | 232-233 | 534 |
| Bidalaka for Paittika Eye-Diseases | 234 | 534 |
| Bidalaka for Kaphaja Eye-Diseases (Gairikadya-Bidalaka) | 235 | 534 |
| Bidalaka for Sannipatika Eye-Diseases | 236 | 535 |
| Ascyotana for Vatika Eye-Diseases | 237 | 535 |
| Eye-Drop for Paittika eye-Diseases | 238 | 535 |
| Ascyotana for Kaphaja and Sannipatika types of Eye-Diseases | 239 | 535 |
| Varti (Bougie) for Vatika Type of Eye-Diseases (Brhatyadi-Varti) | 240 | 536 |
| Varti for Paittika Type of Eye-Diseases (Sumanahkorakadi-Varti) | 241 | 536 |
| Varti for Kaphaja type of Eye-Diseases (Saindhavadi-Varti) | 242 | 536 |
| Varti for Sannipatika Eye-Diseases (Amrtahvadi-Varti) | 243-245 | 537 |
| Recipes for Other Eye-Diseases | 246-251 | 537 |
| Sukhavati-Varti | 252-253 | 538 |
| Drstiprada-Varti | 256-258 | 539 |
| Pippalyadi-Rasakriya | 258-259 | 539 |
| Krsnasarpa-Vasadi-Rasakriya | 259-260 | 540 |
| Other Recipes for Eye-Diseases | 260-262 | 540 |
| Line of Treatment of Hair Diseases | 262-263 | 540 |
| Recipes of Medicated Oil, etc. | 263-268 | 541 |
| Maha-Nila-Taila | 268-276 | 542 |
| Prapaundarikadya-Taila | 276-278 | 543 |
| Ointment for Tawny Hair | 278-279 | 543 |
| Recipe for Restoration of Hair | 279-280 | 543 |
| Treatment of Remaining Head-Diseases | 282 | 544 |
| Treatment of Vatika Svara-Bheda | 283-284 | 545 |
| Treatment of Paittika Svara-Bheda | 285 | 545 |
| Treatment of Kaphaja Svara-Bheda | 286-287 | 546 |
| Treatment of Raktaja Svara-Bheda | 288-289 | 546 |
| Treatment of Sannipatika Svara-Bheda | 290 | 546 |
| Summary | 291 | 547 |
| Micro-cosm and Macro-cosm | 292 | 547 |
| Harmony Among Dosas | 293 | 548 |
| Summary | 294 | 548 |