Vangasena Samhita or Cikitsasara Samgraha Of Vangasena (Two Volumes)
Book Specification
| Item Code: | IDI671 |
| Author: | Dr. Nirmal Saxena |
| Publisher: | Chowkhamba Sanskrit Series Office |
| Language: | (Text with English Translation, Notes, Historical Introduction, Comments, Index and Appendices) |
| Edition: | 2014 |
| ISBN: | 8170801249 |
| Pages: | 1337 |
| Cover: | Hardcover |
| Other Details | 9.7"X 7.3 |
| Weight | 2.27 kg |
Book Description
About The Book
One of the most valuable treasures of Ayurvedic Samhitas, Cikitsasarasamgraha has so far been confined to a few persons. Now the present work is being introduced to bring out its latent knowledge to the English speaking people, particularly for the Western medical practitioners.
This work contains diagnosis, prognosis, symptoms and treatment of the diseases in a very comprehensive manner. Hence it has been divided in two volumes.
Volume I (Nidanadhikara to Slipadarogadhikara)
Volume II (Vidradhi to Dipana-pacanadravya-laksanadhikara) Index & Appendixes
It contains at the end several important appendices on Plants (with Latin names), diseases etc. And a Sanskrit-English glossary of technical terms used in the text, and to crown all this, a valuable deliberation on the entire text by the learned translator.
About The Author
Dr. Nirmal Saxena, is well-known for his out-standing contributions in the fields of Ayurveda and History of Sciences. In the course of nearly twenty eight years dedicated to research the contributed innumerable articles to reputed national and international journals in History, Medicine and Science.
Born on November 4, 1952 in the family of a Vaidya Krishna Kumar, he got his university education at Banaras Hindu University. He completed his Ph. D. On topic, "Development of Indian Medicine from 1400 to 1600 A. D."
Passing through a chequered career of lecturer in History at Triloknath Postgraduate College, Tanda, Faizabad, he joined as Project Investigator under the History of Science Programme of Indian National Science Academy, New Delhi. Completed four projects, 1. "A Critical Study of Yogaratnakara" (1991), 2. "English Translation of Vaidya Jivana of Lolimbaraja" (1996), 3 "English Translation of Camatkara Cintamani of Lolimbaraja" (1999), 4. "English Translation of Vangasena's Cikitsasarasamgraha" (2003), sanctioned by the National Commission for History of Sciences in India.
Preface
One of the most valuable treasures of Ayurvedic Samhitas, Cikitsasarasamgraha has so far been confined to a few persons. Now the present research work is being undertaken by me to bring out its latent knowledge to the English speaking people and particularly for the western medical practitioners.
It will not only prove to be a modern ciritical treatise having historical background but also a book which can be relied on for Indian medical system.
Cikitsasarasamgraha, the immensely valuable text needed since long a faithful and simple translation into English, communicating the ideas as they are without divulging into dogmatic details which make the situation terse particularly for a new scholar.
This work contains diagnosis, prognosis, symptoms and treatment of the diseases in a very comprehensive manner. Hence it has been divided in two Volumes.
Contains following chapters-
Nidanapancakam (The five ways of diagnosis), Jvara-cikitsa (Treatment of fevers), Pitta jvara cikitsa (Treatment of fever due to pitta), Kapha jvara cikitsa (Treatment, of fever due to kapha), Vata pitta jvara cikitsa (Treatment of fever due to vata and pitta), Pitta kapha jvara cikitsa (Treatment of fever caused by pitta and kapha), Vata kapha jvara cikitsa (Treatment of fever caused by vata and kapha), Sannipata jvara cikitsa (Treatment of fever caused by sannipata), Visama jvara (intermittent fever), Jirna jvara (chronic fever), Atisara (diarrhoeas), Grahani disorder, Piles (Haemorrhoids), Indigestion, Visucika (Gestroenteritis), Bhasmaka (excessively digestive fire), Intestinal worms (Helminths), Pandu roga (anaemia), Kamala (Jaundice), Halimaka (chlorosis), Raktapitta (innate haemorrhage), Rajayaksma (Pulmonary tuberculosis - Consumption), Chest - wound and wasting, Cough, Hiccough, Dyspnoea, Hoarseness of voice, Anorexia, Vomiting, Thirst (polydipsia), Fainting, Alcoholism, Burning sensation of the body, Insanity, Epilepsy, Vatavyadhi (Specific vatika disorders, Vatarakta (Gout), Urustambha (Stiffness of the leg); Amavata (Rheumatism), Sula (Colic), Parinamasula (Colic during or after digestion), Udavartta (upward movement of vayu), Anaha (hardness of bowels), Gulma (Abdominal lump), Hrdroga (heart disease), Urograha, Mutrakrcchra (Dysuria), Mutraghata (retention and suppression of urine), Asmari (Vesical calculus), Prameha (Polyurea), Obesity, Udara (abdominal enlargement), Sotha (Oedema), Prameha (Polyurea), Obesity, Udara (abdominal enlargement), Sotha (Oedema), Amtra vrddhi (swellings of the scrotum), Bradhna (scrotal swelling at the junction of lower abdomen (below urinary bladder and scrotum), Galaganda (goitre), Gandamala (cervical adenitis), Granthi (cyst), Arbuda (Tumour), Slipada (filaria).
dravyalaksanadhikarah )
Vidradhi (abscess), Vrana-sotha (Inflammation), Agantuka vrana (Traumatic ulcers), Bhagna (Fracture of bones), Nadi Vrana (sinus), Bhagandara (fistula - in - ano), Upadamsa (soft chancre), Sukadosa (Disorders of penis), Kustha (leprosy and skin diseases), Udarda, sitapitta and kotha (urticaria, skin rashes and erythema, allergy etc.), Amlapitta (acid gastritis), Visarpa (Erysipelas), Visphota (eruptions), Snayuka (guinea worm), Masurika (Chicken pox), Ksudra roga (minor diseases), Mukha roga (Diseases of mouth), Karna - roga (diseases of ear), Nasa - roga (Diseases of nose), Diseases of the eye, Siro - roga (Diseases of head), Stri roga (Diseases of women), Diseases of the eye, Siro - roga (Diseases of head), Stri roga (Diseases of women), Bala roga (Diseases of children), Visa roga (Diseases due to poison), Jaladosadiyogadhikara (Disorders due to water etc.), Rasayanadhikara (Promotive therapy), Vajikarana (aphrodisiacs, Snehapana (unction), Svedadhikara (sudation), Vamanadhikara (emesis), Virecanadhikara (purgation), Bastikarmadhikara (enema), Dhumapana (Smoking), Kavaladhikara (Gargles), Nasyadhikara (Nasal evacuation or snuffing), Svasthavrattadhikara (Ways for keeping good health), Dravyagunadhikara (Properties of drugs), Ganapathadhikara (Description of drug groups), Samsodhana samsamana rasadrvyadinam vargadhikara (Description of drug groups), Samsodhana samsamana rasadrvyadinam vargadhikara (Groups of drugs which are used for purification of body disorders and liquid materials), Dhanyavargadhikara (Groups cereals), Mamsavargadhikara (Properties of meat), Sakaphalavargadhikara (Ordinary food items vegetarian food) and non - vegetarian items of meat, Matsya vyanjanagunadhikara (Properties of food items prepared from fish), Drava-dravyadhikara (Liquid items), Aristadhikara (Signs and symptoms indicative of death of the patient), Dipana pacana dravyalaksanadhikara (Definition of dipana and pacana etc.), Vangasenotpatti.
A historical introduction has also been added in the beginning. At the end following appendices have also been given.
| Preface | iii-iv | |
| Introduction | v-ix | |
| Acknowledgements | xii | |
| Contents | xiii-xiv | |
| | ||
| Chapters | | Page no. |
| 1 | Mangalacaranam | 1 |
| 2 | Nidanapancakam (The five ways of diagnosis) | 2 |
| 3 | Nidanadhikara | 2-19 |
| 4 | Jvara chikitsa (treatment of fevers) | 20-102 |
| 5 | Atisaradhikarah (diarrhoeas) | 103-138 |
| 6 | Grahani disorder | 139-164 |
| 7 | Piles (haemorrhoids) | 165-207 |
| 8 | Indigestion | 208-222 |
| 9 | Visucika (gestroenteritis) | 222-226 |
| 10 | Bhasmaka (excessively intense digestive fire) | 227-228 |
| 11 | Intestinal worms (helminthes) | 229-234 |
| 12 | Pandu roga (anaemia) | 235-249 |
| 13 | Raktapitta (innate haemorrhage) | 250-270 |
| 14 | Rajayaksma (pulmonary tuberculosis-consumption) | 271-287 |
| 15 | Chest - wound and wasting | 288-293 |
| 16 | Cough | 294-314 |
| 17 | Hiccough | 315-319 |
| 18 | Dyspnoea | 320-327 |
| 19 | Hoarseness of voice | 328-331 |
| 20 | Anorexia | 332-337 |
| 21 | Vomiting | 338-346 |
| 22 | Thirst (polydipsia) | 347-352 |
| 23 | Fainting | 353-357 |
| 24 | Alcoholism | 358-365 |
| 25 | Burning sensation of the body | 366-369 |
| 26 | Insanity | 370-382 |
| 27 | Epilepsy | 383-390 |
| 28 | Vatavyadhi (specific vatika disorders) | 391-452 |
| 29 | Vatarakta (gout) | 453-473 |
| 30 | Urustambha (stiffness of the leg) | 474-477 |
| 31 | Amavata (rheumatism) | 478-489 |
| 32 | Sula (colic) | 490-502 |
| 33 | Parinama sula (colic during or after digestion) | 305-513 |
| 34 | Udavarta (upward movement of vayu) | 514-519 |
| 35 | Anaha (hardness of bowels) | 520-522 |
| 36 | Gulma (abdominal tumors) | 523-539 |
| 37 | Hrdroga (heart disease) | 540-546 |
| 38 | Urograha, Mutrakrcchra (dysuria) | 547-554 |
| 39 | Mutraghata (retention and suppression of urine) | 555-561 |
| 40 | Asmari (vesical calculus) | 562-572 |
| 41 | Prameha (polyurea) | 573-586 |
| 42 | Obesity | 587-594 |
| 42 | Udara (abdominal enlargement) | 595-621 |
| 43 | Sotha (oedema) | 622-637 |
| 44 | Amtra-vrddhi (swellings of the scrotum) | 638-644 |
| 45 | Bradhna (scrotal swelling at the junction of lower abdomen (below urinary bladder and scrotum) | 645-646 |
| 46 | Galaganda (goitre) | 647-650 |
| 47 | Gandamala (cervical adenitis) | 651-654 |
| 48 | Granthi (cyst) | 655-658 |
| 49 | Arbuda (tumour) | 659-662 |
| 50 | Slipada (filaria) | 663-669 |
| | ||
| 53 | Vidradhi (abscess) | 671 |
| 54 | Vrana sotha (inflammation) | 678 |
| 55 | Agantuka vrana (traumatic ulcers) (accidental wounds) | 690 |
| 56 | Bhagna (fracture of bones) | 702 |
| 57 | Nadi vrana (sinus) | 707 |
| 58 | Bhagandara (fistula - in - ano) | 713 |
| 59 | Upadamsa (soft chancre) | 718 |
| 60 | Kustha (leprosy and skin diseases) | 729 |
| 61 | Udarda, sitapitta and kotha (urticaria, skin rashes and erythema, allergy etc.) | 762 |
| 62 | Amlapitta (acid gastritis) | 765 |
| 63 | Visarpa (erysipelas) | 775 |
| 64 | Visphota (eruptions) (small pox) | 983 |
| 65 | Snayuka (guinea worm) (thread worm) | 788 |
| 66 | Masurika (chiken pox) | 790 |
| 67 | Ksudra roga (minor diseases) | 801 |
| 68 | Mukha roga (diseases of mouth) | 828 |
| 69 | Karna-roga (diseases of ear) | 855 |
| 70 | Nasa-roga (diseases of nose) | 869 |
| 71 | Disease of eye | 882 |
| 72 | Diseases of siro-roga (head disease) | 945 |
| 73 | Stri roga (diseases of women) | 959 |
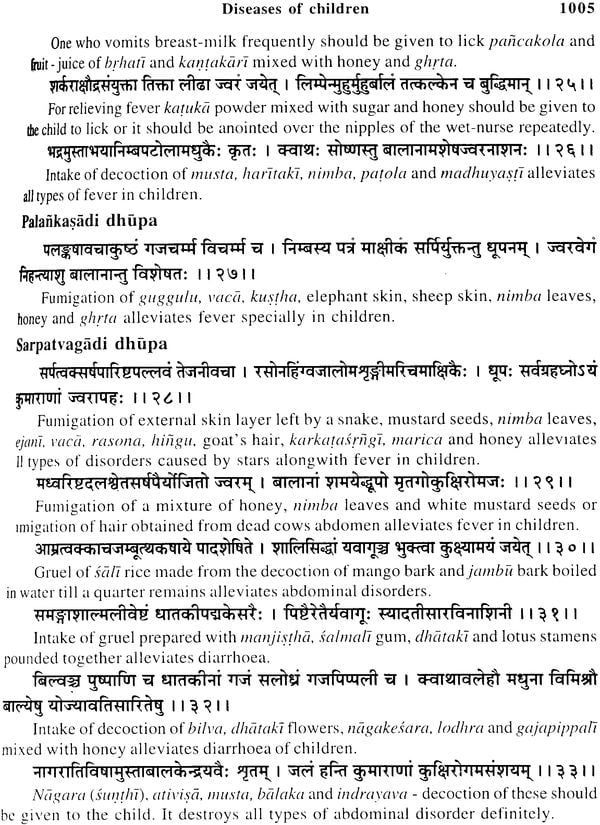
| 74 | Bala roga (diseases of children) | 1002 |
| 75 | Visarogadhikara (diseases due to poison) | 1035 |
| 76 | Jaladosadiyogadhikara (disorders due to water etc.) | 1061 |
| 77 | Rasayanadhikara (promotive therapy) | 1064 |
| 78 | Vajikarana (aphrodisiacs) | 1113 |
| 79 | Snehapana (unction) | 1124 |
| 80 | Svedadhikara (sudation) | 1129 |
| 81 | Vamanadhikara (emesis) | 1132 |
| 82 | Virecanadhikara (purgation) | 1137 |
| 83 | Bastikarmadhikara (enema) | 1145 |
| 84 | Dhumapana (smoking) | 1171 |
| 85 | Kavaladhikara (gargles) | 1175 |
| 86 | Nasyadhikara (nasal evacuation or snuffing) | 1177 |
| 87 | Svasthavrattadhikara (ways for keeping good health) | 1183 |
| 88 | Dravyagunadhikara (properties of drugs) | 1190 |
| 89 | Ganapathadhikara (description of drug groups) | 1200 |
| 90 | Samsodhana samsamana rasadravyadinam vargadhikara (groups of drugs which are used for purification of body, cure of body disorders and liquid materials.) | 1206 |
| 91 | Rtucaryadhikara (seasonal routine - regimen) | 1210 |
| 92 | Dhanyavargadhikara (groups cereals) | 1217 |
| 93 | Mamsavargadhikara (properties of meat) | 1220 |
| 94 | Sakaphalavargadhikara (chapter on vegetables and fruits) | 1223 |
| 95 | Vyanjana - mamsa-vyanjanadhikara [ordinary food items (vegetarian food) and non-vegetarian items of meat] | 1230 |
| 96 | Matsya Vyanjana-gunadhikara (properties of food items prepared from fish) | 1237 |
| 97 | Drava - dravyadhikara (liquid items) | 1241 |
| 98 | Aristadhikara (signs and symptoms indicative of death of the patient) | 1250 |
| 99 | Dipana pacana dravyalaksanadhikara (Definition of dipana and pacana etc.) | 1273 |
| 100 | Vangasenotpatti | 1277 |
| | ||
| Plant names with botanical identification | 1278 | |
| | ||
| Units of weight with metric equivalents | 1307 | |
| | ||
| Diseases mentioned in Vangasen's Cikitsasarasamgraha with their nearest modern equivalents | 1308 |