A Golden Chain of Civilizations-Indic, Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic (Set of 3 Volumes)
Book Specification
| Item Code: | NAF374 |
| Author: | D.P. Chattopadhyaya and G.C. Pande |
| Publisher: | Centre for Studies in Civilizations |
| Language: | English |
| Edition: | 2012 |
| ISBN: | 978818756555 |
| Pages: | 2559 (Throughout B/W and Color Illustrations) |
| Cover: | Hardcover |
| Other Details | 11.0 Inch x 9.0 Inch |
| Weight | 10 gm |
Book Description
Volume 1 Part 4 : A Golden Chain of Civilizations: Indic, Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic Up to 600 Bc
Volume 1 Part 5 : A Golden Chain of Civilizations: Indic, Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic (from c.600 B.c to C.A.D.600)Section 1 : Cultural Contacts and Movements.
VOlume 1 Part 5 : A Golden Chain of Civilizations: Indic, Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic (from c.600 B.c to C.A.D.600) Section 2 : Science, Philosphy and Culture.
The volumes of Project on the History Science, Philosophy and culture in Indian Civilization aim at discovering the main aspect of India’ heritage and present them in an interrelated way. These volumes, in spite of their unitary look, recognize the difference between the areas of material civilization and those of ideational culture. The project is not being executed by a single group of thinkers and writers who are method logically uniform or ideologically identical in their commitments. In fact contributions are made by different scholars with different ideological persuasions and methodological approaches. The project is marked by what may be called methodological pluralism.
The current account of the history of civilization do not generally appear to give adequate importance to non-western civilizations. Works like Needham’s Science and Civilization in China are rare. The accounts of Indic civilization on the other hand have either neglected the factor of civilization contacts or represented them in an inadequate manner. Few serious attempts have been made to gain an insight into human civilization through the comparative historical and integrated studies in all its aspects. Historical research necessarily tied to the study of the source material is still in the process of rising to the level of universal history.
The present volumes, is intended to review the history of science, philosophy and culture in Indian civilization in the context civilization contacts with Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic Worlds and comparable developments in them. The volume is divided into four sections. Proto-History people and language, social and Technological Foundations of Civilization, the most ancient Indian Religion Traditions and birth and rise of science and Philosophy. The focus of the present volume is on science, philosophy and culture, and not on political history or merely regional and epochal developments. It is not intended to give in this volume a general history of civilizations between India and the Mediterranean world but is intended to highlight how contributions were made to the common human quest to Truth, Goodness and beauty under conditions and wide ranging contacts.
The volumes of the PROJECT ON THE HISTORY OF SCIENCE, PHILOSOSPHY AND CULTURE IN INDIAN CMUZATION aim at discovering the main aspects of India's heritage and present them in an interrelated way. These volume insipte of their unitary look, recognize the difference between the areas of material civilizations and those of ideational culture. The project is not being executed by a single group of thinkers and writers who are methodologically uniform or ideologically identical in their commitments. In fact contribution are made by different scholars with different ideological persuasions and methodological approaches. The project is marked by what may be called methodological pluralism.
In spite of its primarily historical character, this project both in its conceptualization and execution has been shaped by scholars drawn from different disciplines. It is for the first time that an Endeavour of such a unique and comprehensive character has been undertaken to study critically major world civilization like India.
The current accounts of the history of civilization do not generally appear to give adequate importance to non western civilization. Works like Needham’s Science and Civilization in china are rare. The accounts of Indic civilization on the hand have either neglected the factor of civilization contacts or represented them in an inadequate manner. New serious attempts have been made to gain an insight into human civilization in all its aspects through the comparative historical and integrated studies. Historical research necessarily tied to the study of the source material is still in the process of rising to the level of universal history. Volume I the sawn and development of Indian civilization comprises six parts. Parts 4 and 5 are intended to review the history of science, philosophy and culture in Indian civilization in the context of civilization contacts with Iranic, semitic and Hellenic worlds and comparable developments in them. Appropriately entitled A golden chain civilization in the context of civilization, part 4 covers the period upto c.600 BC. Part 5 covers the period from c.600 BC to AD 600 in two sections – section I cultural contacts and movements and section 2. Science, Philosophy and culture.
D.P. Chattopadhayaya has studied research law, philosophy and history and taught at various universities in India, Asia, Europe and USA from 1954 to 1994. Founder Chairman of the Indian council of philosophical research (1981-1990) and presidents-cum-chairman of the Indian institute of advanced study, Shimla (1984-1991), Chattopadhyaya is currently the project director of the multidisciplinary 96-volume PHISPC and Chairman of CSC. Among his 35 books, of which he has authored 18 and edtited 17 are individuals and societies; Sri Aurobindo and Karl Marx; Anthroplogy and Historiography of science; Induction, Probability and Historiography of science; Induction, Probability and Skepticism and cultures and Ideologies. He has also held high public offices, namely of Union cabinet minister and state governor. He is a life Member or Russian Academy of Science and a Member of International Institute of Philosophy, Paris.
G.C. Pande thinker, scholar, historian, writer, regarded internationally as an authority on Buddhism and ancient Indian culture, joined the University of Allahabad, his alma mater, as lecturer in the Department of History after receiving his D.Phil in 1947. Later he became Professor and head of the Department of History at three universities Gorakhpur, Rajasthan and Allahabad. He has been the chairmen of Allahabad, Museum Society, Allahabad Indian Institute of advanced studies, Sarnath. The prestigious fellowship of Sahitya Academy has also been conferred on him.
Recipient of many honorary degrees (Vidya Varidhi, Sahitya Vacaspati, Vakpati, Mahamahopadhyaya) and award (Sankara Sammana, Manisha Sammana, Srivani Niyas Alankaran, Murti Devi award, Vishva Bharati Award, Naresh Sammana etc.) he has also been honoured with D. Litt from Banaras Hindu University (2000) and Allahbad University (2003) and is recipient of the first Darshan Vigyan Sammana. Baghirathi brought him the Saraswati Sammana (2004) and Kabir Sammana (2005). He has authored and edited several books and contributed over seventy articles to encyclopedias, anthropologies and journals. His studies in the origins of Buddhism, life and thought of Sankaracharya, studies in Mahayana, foundations of Indian culture, Bharatiya Parampara ke Mool Swara, Vaidika Sanskriti and other books brought him encomiums from scholars such as Gopinath Kaviraj, Vishushekhara Bhattarya, I.B. Horner, H. Nakamura, Louis Renou, Bhikku Pasadika and others.
I
It is understandable that man, shaped by Nature, would like to know Nature. The human ways of knowing Nature are evidently diverse, theoretical and practical, scientific and technological, artistic and spiritual. This diversity has, on scrutiny, been found to be neither exhaustive nor exclusive. The complexity of physical nature, life-world and, particularly, human mind is so enormous that it is futile to follow a single method for comprehending all the aspects of the world in which we are situated.
One need not feel bewildered by the variety and complexity of the worldly phenomena. After all, both from traditional wisdom and our daily experience, we know that our own nature is not quite alien to the structure of the world. Positively speaking, the elements and forces that are out there in the world are also present in our body-mind complex, enabling. us to adjust ourselves to our environment. Not only the natural conditions but also the social conditions of life have instructive similarities between them. This is not to underrate in any way the difference between the human ways of life all over the world. It is partly due to the variation in climatic conditions and partly due to the distinctness of production- related tradition, history and culture.
Three broad approaches are discernible in the works on historiography of civilization, comprising science and technology, art and architecture, social sciences and institutions. Firstly, some writers are primarily interested in discovering the general laws which govern all civilizations spread over different continents. They tend to underplay what they call the noisy local events of the external world and peculiarities of different languages, literatures and histories. Their accent is on the unity of Nature, the unity of science and the unity of mankind. The second group of writers, unlike the generalist or transcendentalist ones, attach primary importance to the distinctiveness of every culture. To these writers human freedom and creativity are extremely important and basic in character. Social institutions and the cultural articulations of human consciousness, they argue, are bound to be expressive of the concerned people's consciousness. By implication they tend to reject concepts like archetypal consciousness, universal mind and providential history. There is a third group of writers who offer a composite picture of civilizations, drawing elements both from their local and common characteristics. Every culture has its local roots and peculiarities. At the same time, it is pointed out that due to demographic migration and immigration over the centuries an element of compositeness emerges almost in every culture. When, due to a natural calamity or political exigencies people move from one part of the world to another, they carry with them, among other things, their language, cultural inheritance and their ways of living. In the light of the above facts, it is not at all surprising that comparative anthropologists and philologists are intrigued by the striking similarity between different language families and the rites, rituals and myths of different peoples. Speculative philosophers of history, heavily relying on the findings of epigraphy, ethnography, archaeology and theology, try to show in very general terms that the particulars and universals of culture are 'essentially' or 'secretly' interrelated. The spiritual aspects of culture like dance and music, beliefs pertaining to life, death and duties, on analysis, are found to be mediated by the material forms of life like weather forecasting, food production, urbanization and invention of script. The transition from the oral culture to the written one was made possible because of the mastery of symbols and rules of measurement. Speech precedes grammar, poetry and prosody. All these show how the 'matters' and 'forms' of life are so subtly interwoven.
II
The PHISPC publications on History of Science, Philosophy and Culture in Indian Civilization, in spite of their unitary look, do recognize the differences between the areas of material civilization and those of ideational culture. It is not a work of a single author. Nor is it being executed by a group of thinkers and writers who are methodologically uniform or ideologically identical in their commitments. In conceiving the Project we have interacted with, and been influenced by, the writings and views of many Indian and non- Indian thinkers.
The attempted unity of this Project lies in its aim and inspiration. We have in India many scholarly works written by Indians on different aspects of our civilization and culture. Right from the pre-Christian era to our own time, India has drawn the attention of various countries of Asia, Europe and Africa. Some of these writings are objective and informative and many others are based on insufficient information and hearsay, and therefore not quite reliable, but they have their own value. Quality and view-points keep on changing not only because of the adequacy and inadequacy of evidence but also, and perhaps more so, because of the bias and prejudice, religious and political conviction, of the writers.
Besides, it is to be remembered that history, like Nature, is not an open book to be read alike by all. The past is mainly enclosed and only partially disclosed. History is, therefore, partly objective or 'real' and largely a matter of construction. This is one of the reasons why some historians themselves think that it is a form of literature or art. However, it does not mean that historical construction is 'anarchic' and arbitrary. Certainly, imagination plays an important role in it.
But its character is basically dependent upon. the questions which the historian raises and wants to understand or answer in terms of the ideas and actions of human beings in the past ages. In a way, history, somewhat like the natural sciences, is engaged in answering questions and in exploring relationships of cause and effect between events and developments across time. While in the natural sciences, the scientist poses questions about nature in the form of hypotheses, expecting to elicit authoritative answers to such questions, the historian studies the past, partly for the sake of understanding it for its own sake and partly also for the light which the past throws upon the present, and the possibilities which it opens up for moulding the future. But the difference between the two approaches must not be lost sight of. The scientist is primarily interested in discovering laws and framing theories, in terms of which different events and processes can be connected and anticipated. His interest in the conditions or circumstances attending the concerned events is secondary. Therefore, scientific laws turn out to be basically abstract and easily expressible in terms of mathematical language. In contrast, the historian's main interest centers round the specific events, human ideas and actions, not general laws. So, the historian, unlike the scientist, is obliged to pay primary attention to the circumstances of the events he wants to study. Consequently, history, like most other humanistic disciplines, is concrete and particularistic. This is not to deny the obvious truth that historical event and processes consisting of human ideas and actions show some trend or other and weave some pattern or another. If these trends and patterns were not there at all in history, the study of history as a branch of knowledge would not have been profitable or instructive. But one must recognize that historical trends and patterns, unlike scientific laws and theories, are not general or purported to be universal in their scope.
III
The aim of this Project is to discover the main aspects of Indian culture and present them in an interrelated way. Since our culture has influenced, and has been influenced by, the neighboring cultures of West Asia, Central Asia, East Asia and Southeast Asia, attempts have been made here to trace and study these influences in their mutuality. It is well-known that during the last three centuries, European presence in India, both political and cultural, has been very widespread. In many volumes of the Project considerable attention has been paid to Europe and through Europe to other parts of the world. For the purpose of a comprehensive cultural study of India, the existing political boundaries of the South Asia of today are more of a hindrance than help. Cultures, like languages, often transcend the bounds of changing political territories.
If the inconstant political geography is not a reliable help to the understanding of the layered structure and spread of culture, a somewhat comparable problem is encountered in the area of historical periodization. Periodization or segmenting time is a very tricky affair. When exactly one period ends and another begins is not precisely ascertainable. The periods of history designated as ancient, medieval and modern are purely conventional and merely heuristic in character. The varying scopes of history, local, national and continental or, universal, somewhat like the periods of history, are unavoidably fuzzy and shifting. Amidst all these difficulties, the volume-wise details have been planned and worked out by the editors in consultation with the Project Director and the General Editor. I believe that the editors of different volumes have also profited from the reactions and suggestions of the contributors of individual chapters in planning the volumes.
Another aspect of Indian history which the volume-editors and contributors of the Project have carefully dealt with is the distinction and relation between civilization and culture. The material conditions which substantially shaped Indian civilization have been discussed in detail. From agriculture and industry to metallurgy and technology, from physics and chemical practices to the life sciences and different systems of medicines- all the branches of knowledge and skill which directly affect human life- form the heart of this Project. Since the periods covered by the PHISPC are extensive-prehistory, proto-history, early history, medieval history and modern history of India-we do not claim to have gone into all the relevant material conditions of human life. We had to be selective. Therefore, one should not be surprised if one finds that only some material aspects of Indian civilization have received our pointed attention, while the rest have been dealt with in principle or only alluded to.
One of the main aims of the Project has been to spell out the first principles of the philosophy of different schools, both pro-Vedic and anti-Vedic. The basic ideas of Buddhism, Jainism and Islam have been given their due importance. The special position accorded to philosophy is to be understood partly in terms of its proclaimed unifying character and partly to be explained in terms of the fact that different philosophical systems represent alternative world-views, cultural perspectives, their conflict and mutual assimilation.
Most of the volume-editors, and at their instance the concerned contributors, have followed a middle path between the extremes of narrativism and theoreticism. The underlying idea has been this: if in the process of working out a comprehensive Project like this every contributor attempts to narrate all those interesting things that he has in the back of his mind, the enterprise is likely to prove unmanageable. If, on the other hand, particular details are consciously forced into a fixed mould or pre-supposed theoretical structure, the details lose their particularity and interesting character. Therefore, depending on the nature of the problem of discourse, most of the writers have tried to reconcile in their presentation, the specificity of narrativism and the generality of theoretical orientation. This is a conscious editorial decision. Because, in the absence of a theory, however inarticulate it may be, the factual details tend to fall apart. Spiritual network or theoretical orientation makes historical details not only meaningful but also interesting and enjoyable.
Another editorial decision which deserves spelling out is the necessity or avoid ability of duplication of the same theme in different volumes or even in the same volume. Certainly, this Project is not an assortment of several volumes. Nor is any volume intended to be a miscellany. This Project has been designed with a definite end in view and has a structure of its own. The character of the structure has admittedly been influenced by the variety of the themes accommodated within it. Again it must be understood that the complexity of structure is rooted in the aimed integrality of the Project itself.
IV
Long and in-depth editorial discussion has led us to several unanimous conclusions. Firstly, our Project is going" to be unique, unrivalled and discursive in its attempt to integrate different forms of science, technology, philosophy and culture. Its comprehensive scope, continuous character and accent on culture distinguish it from the works of such Indian authors as P.C. Ray, B.N. Seal, Binoy Kumar Sarkar and S.N. Sen and also from such Euro-American writers as Lynn Thorndike, George Sarton and Joseph Needham. Indeed, it would be no exaggeration to suggest that it is for the first time that an Endeavour of so comprehensive a character, in its exploration of the social, philosophical and cultural characteristics of a distinctive world civilization-that of India-has been attempted in the domain of scholarship.
Secondly, we try to show the linkages between different branches of learning as different modes of experience in an organic manner and without resorting to a kind of reductionism, materialistic or spiritualistic. The internal dialectics of organics without reductionism allows fuzziness, discontinuity and discreteness within limits.
Thirdly, positively speaking, different modes of human experience-scientific, artistic, etc.-have their own individuality, not necessarily autonomy. Since all these modes are modification and articulation of human experience, these are bound to have between them some finely graded commonness. At the same time, it has been recognized that reflection on different areas of experience and investigation brings to light new insights and findings. Growth of knowledge requires humans, in general, and scholars, in particular, to identify the distinctness of different branches of learning.
Fourthly, to follow simultaneously the twin principles of: (a) individuality of human experience as a whole, and (b) individuality of diverse disciplines, is not at all an easy task. Overlap of themes and duplication of the terms of discourse become unavoidable at times. For example, in the context of Dharmasistra, the writer is bound to discuss the concept of value. The same concept also figures in economic discourse and also occurs in a discussion on fine arts. The conscious editorial decision has been that, while duplication should be kept to its minimum, for the sake of intended clarity of the themes under discussion, their reiteration must not be avoided at high intellectual cost.
Fifthly, the scholars working on the Project are drawn from widely different disciplines. They have brought to our notice an important fact that has clear relevance to our work. Many of our contemporary disciplines like economics and sociology did not exist, at least not in their present form, just two centuries ago or so. For example, before the middle of the nineteenth century, sociology as a distinct branch of knowledge was unknown. The term is said to have been coined first by the French philosopher Auguste Comte in 1838. Obviously, this does not mean that the issues discussed in sociology were not there. Similarly, Adam Smith's (1723-90) famous work The Wealth of Nations is often referred to as the first authoritative statement of the principles of (what we now call) economics. Interestingly enough, the author was equally interested in ethics and jurisprudence. It is clear from history that the nature and scope of different disciplines undergo change, at times very radically, over time. For example, in ancients India arthasiistra did not mean the science of economics as understood today. Besides the principles of economics, the Arthasiistra of Kautilya discusses at length those of governance, diplomacy and military science.
Sixthly, this brings us to the next editorial policy followed in the Project. We have tried to remain very conscious of what may be called indeterminacy or inexactness of translation. When a word or expression of one language is translated into another, some loss of meaning or exactitude seems to be unavoidable. This is true not only in the bilingual relations like Sanskrit-English and Sanskrit-Arabic, but also in those of Hindi-Tamil and Hindi-Bengali. In recognition of the importance of language-bound and context-relative character of meaning we have solicited from many learned scholars, contributions written in vernacular languages. In order to minimize the miseffect of semantic inexactitude we have solicited translational help of that type of bilingual scholars who know both English and the concerned vernacular language, Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Bengali or Marathi.
Seventhly and finally, perhaps the place of technology as a branch of knowledge in the composite universe of science and art merits some elucidation. Technology has been conceived in very many ways, e.g., as autonomous, as 'standing reserve', as liberating or enlarge mental, and alimentative or estrange mental force. The studies undertaken by the Project show that, in spite of its much emphasized mechanical and alienative characteristics, technology embodies a very useful mode of knowledge that is peculiar to man. The Greek root words of technology are techne (art) and logos (science). This is the basic justification of recognizing technology as closely related to both epistemology, the discipline of valid knowledge, and axiology, the discipline of freedom and values. It is in this context that we are reminded of the definition of man as homo technikos. In Sanskrit, the word closest to techne is kala which means any practical art, any mechanical or fine art. In the Indian tradition, in Saiuatantra, for example, among the arts (kala) are counted dance, drama, music, architecture, metallurgy, knowledge of dictionary, encyclopedia and prosody. The closeness of the relation between arts and sciences, technology and other forms of knowledge are evident from these examples and was known to the ancient people. The human quest for knowledge involves the use of both head and hand. Without mind, the body is a corpse and the disembodied mind is a bare abstraction. Even for our appreciation of what is beautiful and the creation of what is valuable, we are required to exercise both our intellectual competence and physical capacity. In a manner of speaking, one might rightly affirm that our psychosomatic structure is a functional connector between what we are and what we could be, between the physical and the beyond. To suppose that there is a clear-cut distinction between the physical world and the psychosomatic one amount to denial of the possible emergence of higher Iogico-mathematical, musical and other capacities. The very availability of aesthetic experience and creation proves that the supposed distinction is somehow overcome by what may be called the bodily self or embodied mind.
Volume I
| Editors | xi | |
| General Introduction | xiii | |
| Contributors | xxiii | |
| Introduction | xxvii | |
| Section I | ||
| Proto-Historic People and Language | ||
| 1 | Trail of Proto-Indo-Europeans: Archaeological Evidence | 3 |
| 2 | The Problem of the Aryan People and their Language | 29 |
| 3 | Comparative Philology in Modern Linguistics | 66 |
| 4 | Indentifying the Rgvedic People - An Archaeological Approach | 80 |
| Section II | ||
| Social and Technological Foundations of Civilizations | ||
| 5 | Theories of the Nature, Origin and Spread of Civilization-Traditional and Modern | 111 |
| 6 | Food Production and Settlements Transition from Neolithic to the Chalcolithic: the Indian scene | 132 |
| 7 | The Tool Technology and the Interactive Mechanisms: Reflection from the Chalcolithic Culture of India | 150 |
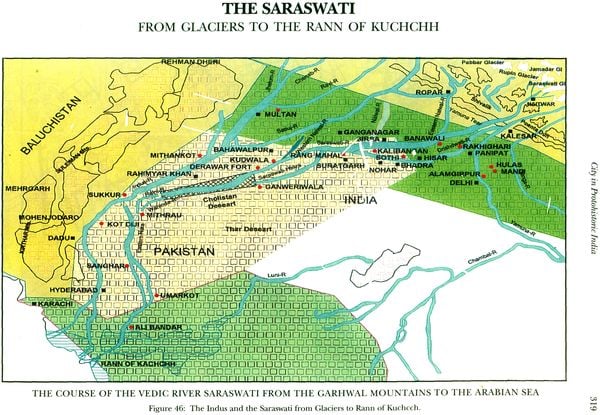
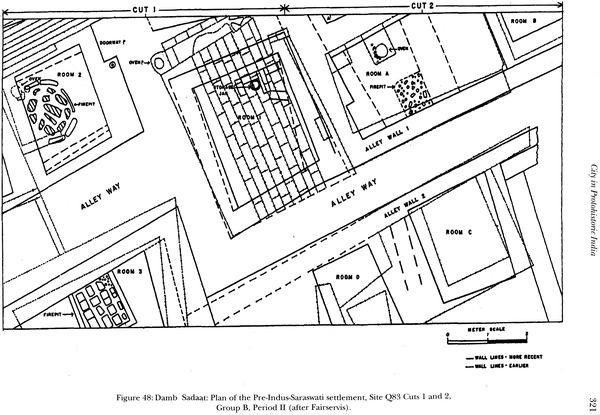
| 8 | City in Protohistoric India | 209 |
| 9 | Ancient Metallurgy of gold in Indic, Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic Civilizations | 356 |
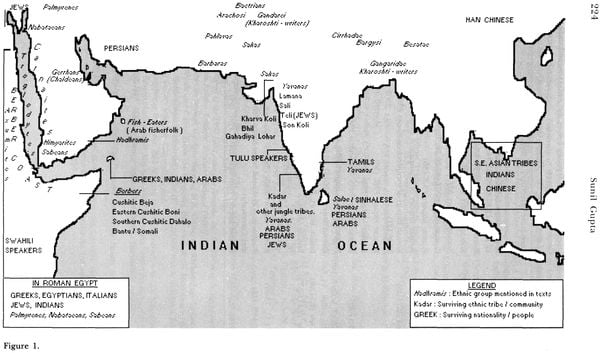
| 10 | Trade and Trade mechnisms in Ancient Civilizations: The early Indian Ocean world 3000 Bc-AD 300 | 417 |
| 11 | Indo-European and indo-Iranian Social Organization | 441 |
| Section III | ||
| The Most Ancient Indian Religion Traditions | ||
| 12 | Cosmogonic Myths of Indo-Europens | 477 |
| 13 | Glimpses of Vedic Cosmololgy | 497 |
| 14 | Vedic, Mesopotamian and Egyptin Religio-Philosophy Thought | 508 |
| 15 | Akhenaten, Surya, and the Rgveda | 618 |
| 16 | Movements of Ethical and Spiritual Enlightenment: Early Judaism | 639 |
| Section IV | ||
| Birth and Rise of Science and Philosophy | ||
| 17 | Astronomical observations in the vedas | 763 |
| 18 | Astronomical Observation in later samhitas, Brahmans and sutra-literature | 716 |
| 19 | Astronomical Meaning of the vedas | 810 |
| 20 | Babylonian and Indian Astronomy: Early Connections | 826 |
| 21 | Interaction between Greek and Indian Science | 849 |
| 22 | The Irrational in Indian and Greek Mathematical Thought | 874 |
| 23 | Greek Philosophy up to Aristotle | 902 |
| 24 | The Dawn of Philosophy: Comparisons between ancient Greek and Indian Thought | 948 |
| 25 | Formal logic in ancient India and Greece | 956 |
| 26 | Science of Interpretation | 994 |
| 27 | Origin of writing: A Historiographical Appraisal | 1066 |
| Index | 1173 |
Volume II
| Editors | ix | |
| General Introduction | xi | |
| Contributions | xxi | |
| Diacritics for Transliteration | xxiv | |
| Introduction | xxv | |
| 1 | Phythagoras and India | 1 |
| 2 | Alexander and the Hellenistic Empire | 27 |
| 3 | Greek Authors on Ancient India | 81 |
| 4 | Aristole's Theory of Drama | 123 |
| 5 | Philosophy in Hellenistic and Roman times | 149 |
| 6 | Ancient Indian Trade with the Roman World: And an Archaeohistorical Construction | 205 |
| 7 | Prophet Zarathustra the Avesta and the vedas | 229 |
| 8 | The Ancient Riligion of Iran and Reforms by Prophet of Zarathustra | 249 |
| 9 | Iranian Empire : Indus to Mediterranean | 265 |
| 10 | Sasanian Political History, Society and Art | 301 |
| 11 | Ethnic Movements from central Asia: The Sakas and the Pahlavas | 319 |
| 12 | Migrations from central Asia: The Kushans | 357 |
| 13 | Economy and Social Stracture in Central Asia in the Kushan Peried | 379 |
| 14 | Urbanization in the Kushan Empire | 389 |
| 15 | The Kushans and Urbanization in Afghanistan | 399 |
| 16 | The Religion Universe of the Kushan Empire | 407 |
| 17 | The Kushans and the Sun-Cult | 407 |
| 18 | Buddhist Arhaeology in Kushan and Kashano-Sassanian Afghanistan | 435 |
| 19 | Art in the Kushan Empire | 443 |
| 20 | The Contribution of the Kushan period in Language and Literature | 463 |
| 21 | Kushan Archaeology vis-à-vis Kushan Civilization in Afghanistan Problem and Perspectives | 469 |
| 22 | Sakas in India | 479 |
| Index | 521 |
Volume III
| Editors | ||
| General Introduction | ||
| Contributors | ||
| Diacritics for Transliteration | ||
| Introduction | ||
| 1 | Concept and taxonomy of knowledge: A Note | 1 |
| 2 | Social Background and role of science in Ancient Civilization: Indic, Iranic, Semitic and Hellenic | 17 |
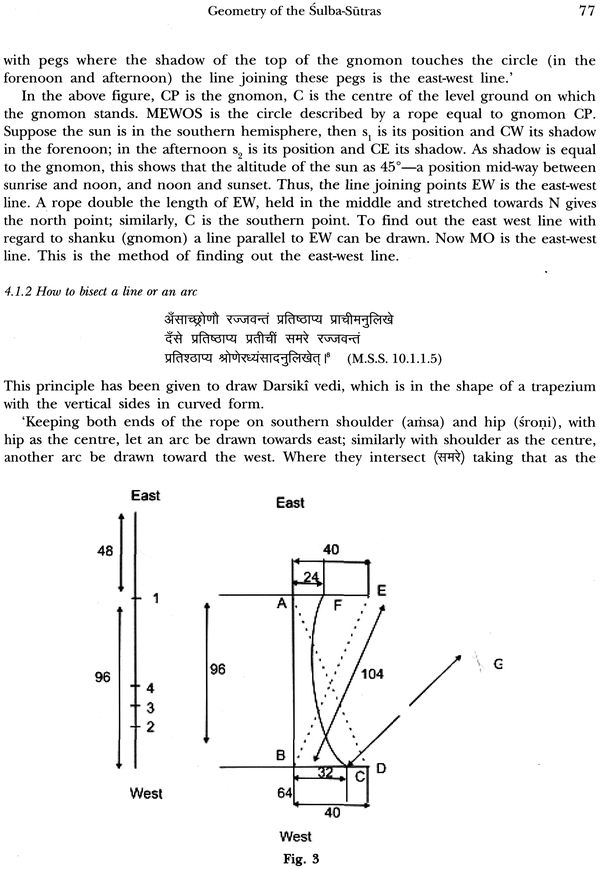
| 3 | Geometry of the Sulba Sutras | 69 |
| 4 | The Astronomy of Five Siddantas | 139 |
| 5 | Ancient Indian Mahematics | 225 |
| 6 | Ancient Indian Astronomy | 273 |
| 7 | Hisab Al-Hind | 321 |
| 8 | Acharya Varahmihir: His Life and Time | 339 |
| 9 | Anatomy ans Surgery in Ayurveda | 367 |
| 10 | Therapeutic use of Aromatic Products in Ancient Indian Cosmetics and Perfumes | 397 |
| 11 | Scientific Temper of Upanisadic Sprituality | 415 |
| 12 | Bhartrhari as a Grammarian and Philosopher | 425 |
| 13 | Vaisesika System | 495 |
| 14 | Jaina Metaphysics and Logic | 525 |
| 15 | Origin and Development of the Schools of Abhidhamma with Special Reference to Theravada School of Abhidhamma | 567 |
| 16 | Early Evidence of Female figures, Music and Dance | 591 |
| 17 | The Rise of Christianity up tp Emperor Constantine | 699 |
| 18 | Meeting of Art Traditions: Gandhara and Mathura (Up to AD 600) | 733 |
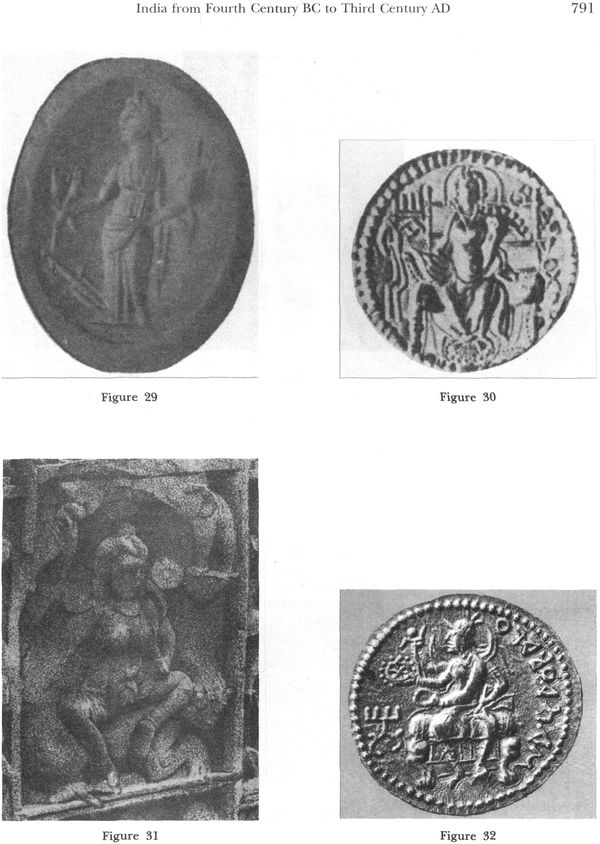
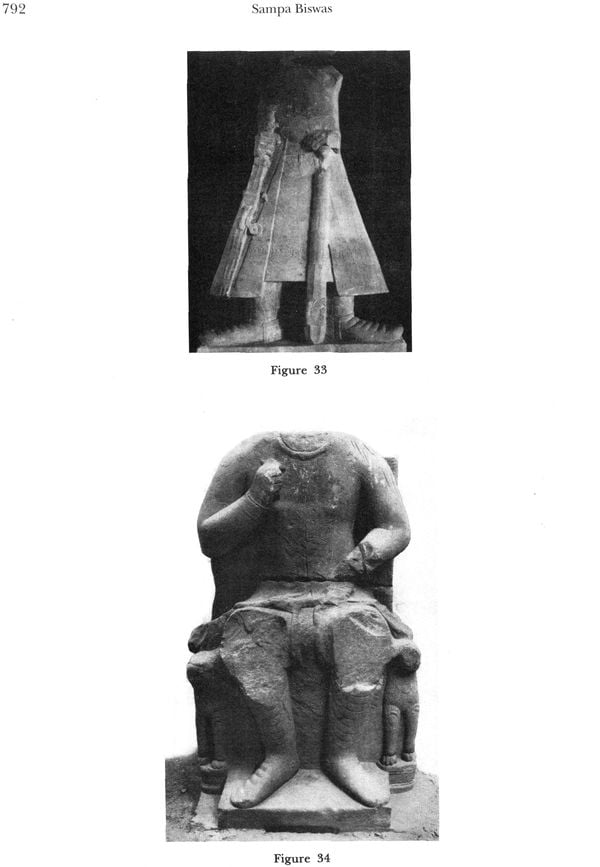
| 19 | India from Fourth Century BC to Third Century AD: Cultural and Artistic Links with Greece central West Asia | 763 |
| Index | 793 |