An Illustrated Text Book of Agada Tantra
Book Specification
| Item Code: | IDJ014 |
| Author: | Dr. U. R. Sekhar Namburi |
| Publisher: | Chaukhambha Sansrit Bhawan |
| Language: | English |
| Edition: | 2015 |
| ISBN: | 8186937781 |
| Pages: | 325 (Color llustrations 34) |
| Cover: | Paperback |
| Other Details | 8.5" X 5.5" |
| Weight | 320 gm |
Book Description
PREFACE
I always wonder why the student find themselves in a state of uncertainty, lack of direction and approach at the time of examination as well as in clinical practice.
I think there are two reasons for this. First and most important reason in not understanding the basic concept of the clinical problem. The second reason is lack of proper text books.
This is a humble effort to generate such an interest towards practical knowledge in the treatment of the poisoning.
The sole interest of the book is to provide the essential contents of toxicology for undergraduates. Throughout the book care has been taken and the subject is presented in such a way that the fundamentals of the subject will be understood easily.
An attempt has been made to explain right from, history till clinical condition including origin, types, etiopathogenesis etc. of poisoning. Practical perspectives towards the diagnosis, investigations and management according to Ayurveda and contemporary science are also elaborated.
Number of diagrams, flowcharts and illustrations have been included wherever required for better understanding of the subject. I have reviewed various textbooks and journals in presentation of the book. I am a grateful to all those authors. Suggestions and criticism from readers will help me in improving this book in subsequent editions. I feel that my efforts are fruitful. If this is found to be useful by medical students and others concerned with toxicological matters.
My vocabulary is insufficient to express the gratefulness to Dr. D. Veerendra Heggade, president of S.D.M.E.S. AT these moments I extend my deepest gratitude towards our respected secretary Prof. S. Prabhakar and beloved principal Dr. Prasanna. N. Rao without whose inspiration the work would not have been succeeded.
I avail the opportunity to thank Prof. Dr. B. Srinivas Prasad and Prof. Dr. D. Lakshamanachari who showed the path and direction for a sincere work.
I am also thankful to my colleagues, student Dr. Chidanand Patwardhan and my computer engineer Mr. Subramanya.
Petty words are unable to convey even a fraction of gratitude and honour towards my parents, Ammaji, Swamiji. Their holiness is the polestar of my life.
Last but not the least my thanks to my wife Dr. Shilpa Sekhar for all her support.
Ayurveda, the Ancient Indian Medical Science, is rapidly gaining global acceptability as a highly effective Healthcare sys- tem. It is one of the most complex and intellectually challenging. among Professional pursuits, demanding as effective integration of one of the World's oldest systems of Medicine with the ad- vancements and needs of the current era.
Agada Tantra (Toxicology) was so highly developed during the early ages that it was given prime status, as one among the eight branches of Classical Ayurveda. It still continues to serve successfully Rural publications, especially in treating snake bites, in areas where Anti-venom is not readily available.
Learning Ayurveda without the knowledge of Sanskrit has become a difficult task for modern students. Though a strong working knowledge of Sanskrit is an essential requisite for a comprehensive understanding of Ayurveda, teaching Ayurveda through the English language can be effective and valuable first step towards Ayurvedic Education, especially for the beginners. This book is the first of its kind, where an effort has been made to bring out a volume on Agada Tantra in English, specifically de- signed to meet the requirements of the Central Council of Indian Medicine (CCIM) Syllabus norms.
In an appreciable and unique effort, the Author has com- piled the Ancient subject from the sources scattered throughout original Ayurvedic literature and has also systematically organised the data in the Textbook with a modern perspective.
Times have changed and advances have to be made accordingly, without comprising the fundamentals of Ancient Knowledge. New concepts may be introduced to enrich the science as well as to contribute to current Healthcare challenges. Environmental pollution and vast changes in dietary habit have led to gradual accumulation of toxins in the body, with potential long- term health hazards. Ayurveda has accorded high priority for this type of toxicity, and prescribes various therapeutic measures for detoxification, mainly Panchakarma. Incorporation of these modern toxic hazards and their treatment into the framework of Agada Tantra are topics which merit debate amongst experts in the field. Such studies will contribute significantly towards Healthcare of people of the current era as well as future generations.
This is need for many such books as this, in all branches of Ayurveda.
| 1 | INTRODUCTION TO AGADA TANTRA | |
| I) INTRODUCTION | 01 | |
| II) HISTORICAL REFERENCES OF VISA | 01 | |
| III) DERIVATION | 02 | |
| IV) DEFINITION | 03 | |
| V) IMPORTANCE | 04 | |
| 2 | INTRODUCTION TO VISA | |
| I) DERIVATION OF VISA | 06 | |
| II) DEFINATION OF VISA | 06 | |
| III) SYNONYMS OF VISA | 07 | |
| IV) MYTHOLOGICAL ORIGIN OF VISA | 07 | |
| V) FORM OF ORIGIN OF VISA | 10 | |
| VI) SITES OF VISA | 10 | |
| VII) MOVEMENTS OF VISA | 13 | |
| 3 | CLASSIFICATION OF POISON | |
| I) ACCORDING TO AYURVEDA | 14 | |
| II) ACCORDING TO MODERN | 17 | |
| III)POISONING | 19 | |
| 4 | PROPERTIES AND ACTION OF POISON | |
| I) PROPERTIES OF POISON | 22 | |
| II) PROPERTIES OF OJAS | 25 | |
| III) DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VISA,MADYA & OJAS | 26 | |
| IV) ADMINISTRATION OF THE POISON | 26 | |
| V) ACTION OF THE POISON ON THE BODY | 29 | |
| VI) FACTORS MODIFYING ACTION OF THE POISON | 30 | |
| VII) EFFECT OF POISON ON THE BODY | 33 | |
| VIII) ROLE OF POISON IN VITIATING THE DOSAS | 35 | |
| IX) SPREADING OF THE POISON IN THE BODY | 35 | |
| X) SEVERITY OF POISON | 36 | |
| XI) IMPULSE OF THE POISON | 36 | |
| XII) VISA VEGANTARA | 36 | |
| XIII) POISONOUS IMPULSE GENERAL FEATURES | 37 | |
| XIV) ROUTES OF ELIMINATION OF POISON | 39 | |
| XV) CRITICAL / FATAL PERIOD IN POISONING | 40 | |
| 5 | DIAGNOSIS OF POISING | |
| I) ACCORDING TO AYURVEDA | 41 | |
| II) ACCORDING TO MODERN | 42 | |
| III) DUTIES OF MEDICAL PRACTITIONER IN CASE OF SUSPECTED POISONING | 50 | |
| 6 | TREATMENT OF POISON | |
| I) ASSESSMENT OF THE PATIENT'S CONDITION | 54 | |
| II) TREATMENT | 57 | |
| III) FEATURES OF RECOVERY FROM THE POISONING | 86 | |
| 7 | COMPLICATIONS OF POISONING | |
| I) POISONING COMPLICATIONS | 93 | |
| 8 | VEGETABLE AND STATIC POISONS | |
| I) VEGETABLE POISON GENERAL FEATURES | 98 | |
| II) FEATURES OF VEGETABLE POISON ACCORDING TO SITE | 98 | |
| III) FEATURES OF THE VEGETABLE POISON IMPULSES | 100 | |
| IV) TREATMENT OF VEGETABLE POISON ACCORDING TO THE IMPULSE ADMINISTRATION OF THE POISON | 102 | |
| V) TREATMENT OF POISONING ACCORDING TO SITE | 105 | |
| 9 | IMPOVERISHED OR WEAK POISONS | |
| I) INTRODUCTION | 173 | |
| II) DERIVATION | 173 | |
| III) DEFINATION | 173 | |
| IV) ETIOLOGY | 174 | |
| V) AGGRAVATING TIME | 174 | |
| VI) PRODORMAL FEATURES | 175 | |
| VII) FEATURES | 175 | |
| VIII) FEATURES ACCORDING TO SITE | 175 | |
| IX) IMPACT OF DUSIVISA | 175 | |
| X) PROGNOSIS | 176 | |
| XI) TREATMENT | 176 | |
| XII) TREATMENT FOR COMPLICATIONS | 177 | |
| 10 | ARTIFICIAL POISON | |
| I) DERIVATION | 178 | |
| II) DEFINATION | 178 | |
| III) METHOD OF POISONING | 179 | |
| IV) FEATURES | 179 | |
| V) PROGNOSIS | 180 | |
| VI) TREATMENT | 180 | |
| 11 | ALCOHOL POISONING | |
| I) DERIVATION | 182 | |
| II) DEFINITION | 182 | |
| III) PROPERTIES OF ALCOHOL | 183 | |
| IV) MERITS AND DEMERITS OF ALCOHOL | 184 | |
| V) EFFECT OF THE ALCOHOL ON THE BODY | 186 | |
| VI) STAGES OF MADA | 187 | |
| VII) MADYAPANA VIKARAS | 189 | |
| VIII) TREATMENT | 192 | |
| IX) POSTMORTEM APPEARANCE | 205 | |
| X) MEDICO-LEGAL IMPORTANCE | 206 | |
| 12 | SNAKE POISON | |
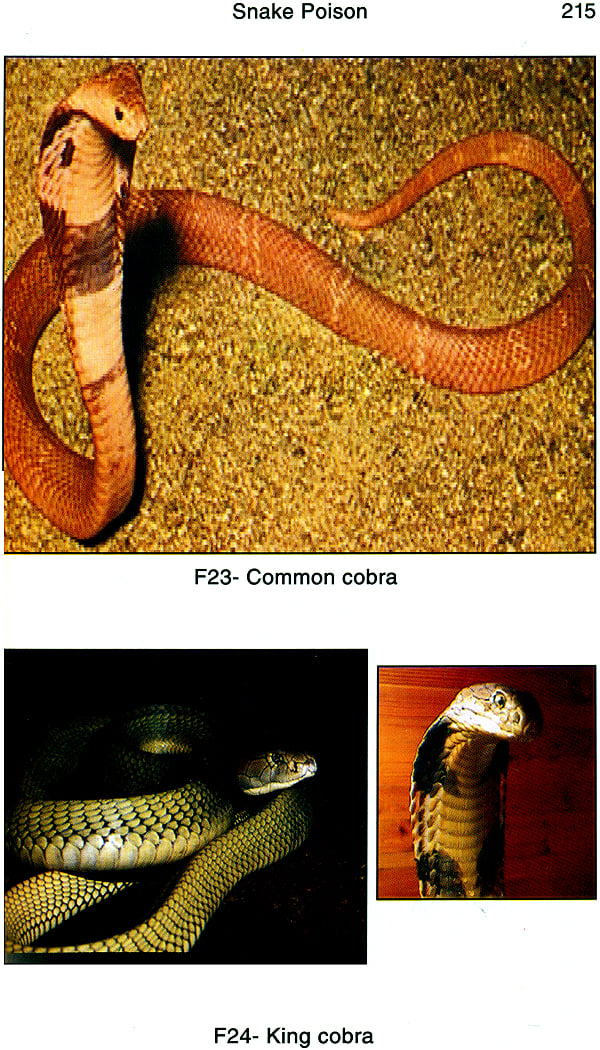
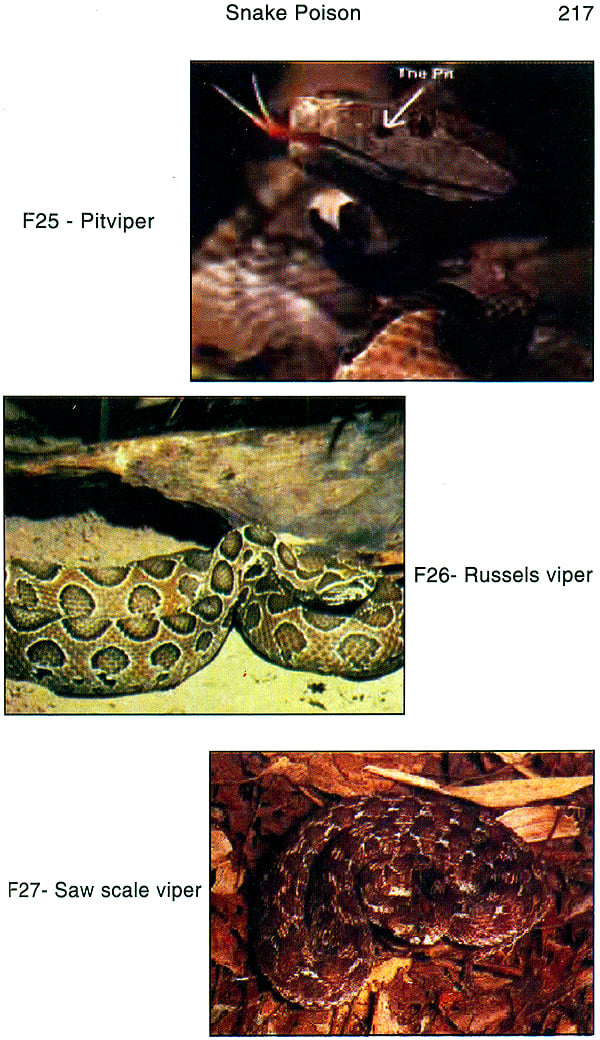
| I) CLASSIFICATION OF THE SNAKES | 208 | |
| II) SNAKES REPRODUCTION | 218 | |
| III) IDENTIFICATION OF THE SNAKES | 220 | |
| IV) FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE IN THE INCREASE IN THE POTENCY OF THE SNAKE POISON | 222 | |
| V) FACTORS INFLUENCE IN THE DECREASE IN THE POTENCY OF THE SNAKE POISON | 223 | |
| VI) FACTORS INFLUENCING THE SNALE BITE | 223 | |
| VII) TYPES OF THE SNAKES BITE | 224 | |
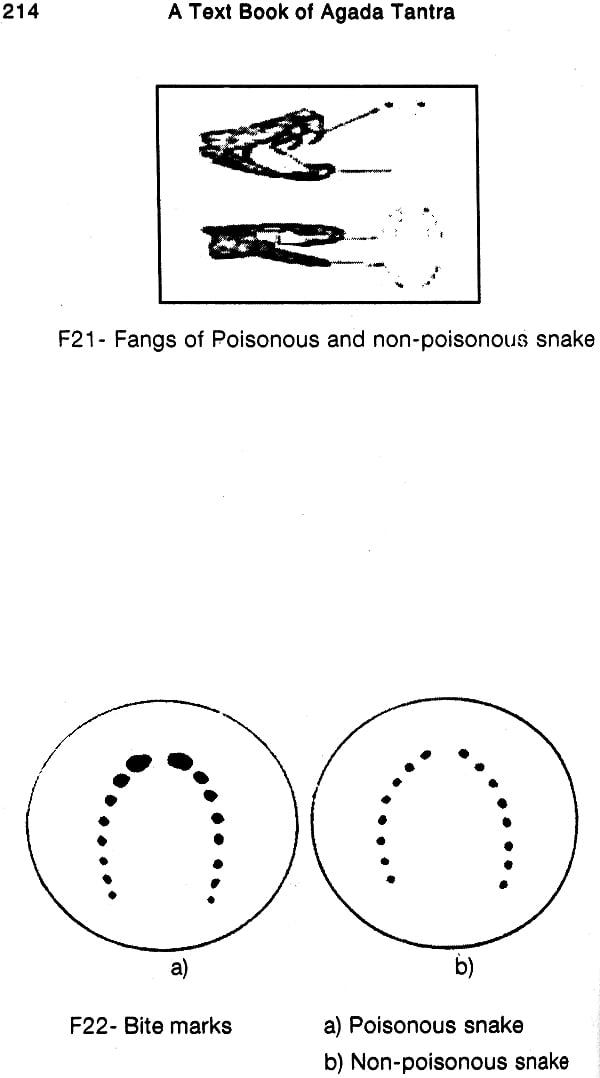
| VIII) DIFFERENCE BETWEEN POISONOUS AND NON-POISON SNAKE BITE | 225 | |
| IX) DIFFERENT POISONOUS SNAKE BITE FEATURES | 226 | |
| X) SNAKE POISON IMPULSES | 229 | |
| XI) REJECTABLE PATIENT | 236 | |
| XII) TREATMENT | 237 | |
| 13 | RABIES POISON | |
| I) CAUSES | 256 | |
| II) FEATURES | 256 | |
| III) TREATMENT | 256 | |
| IV) SOME OF THE REMEDIES,PREPARATIONS OF MEDICINES AND TREATMENT IN ALARKA VISA | 259 | |
| 14 | SCORPION POISONING | |
| I) CLASSIFICATION OF SCORPION | 267 | |
| II) POISONING FEATURES | 268 | |
| III) TREATMENT | 269 | |
| IV) SOME OF THE ANTI-POISONOUS THERAPEUTICS FROM THE YOGARATNAKARAADMINISTRATION OF THE POISON | 271 | |
| 15 | SPIDER POISON | |
| I) MYTHOLOGICAL ACCOUNT OF THE ORIGIN | 275 | |
| II) CLASSIFICATION OF LUTA | 275 | |
| III) SITE OF POISON IN LUTA | 276 | |
| IV) CLINICAL FEATURES | 276 | |
| V) TREATMENT | 281 | |
| VI) SPECIFIC MANAGEMENT FOR DIFFERENT LUTAS | 283 | |
| 16 | KITAVISA | |
| I) ORIGINATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF KITA | 290 | |
| II) SHARP INSECT POISONOUS FEATURES | 290 | |
| III) MILD INSECT POISONOUS FEATURES | 291 | |
| IV) TREATMENT | 291 | |
| 17 | FOOD POISONING | 299 |
| 18 | POISONING INDIA | 311 |
| BIBLIOGRAPHY | 317 | |
| INDEX | 321 | |
| LIST OF FIGURES | XV |