Blood and Liver Disorders (Ayurvedic and Modern Concept)
Book Specification
| Item Code: | NAE142 |
| Author: | Dr. V. B Athavale& Dr. Kamlesh V. Athavale |
| Publisher: | Sanatan Bharatiya Sanskriti Sanstha |
| Edition: | 2002 |
| ISBN: | 8180490165 |
| Pages: | 174 (10 Throughout Color Illustrations) |
| Cover: | Paperback |
| Other Details | 8.5 inch X 5.5 inch |
| Weight | 200 gm |
Book Description
Dr. Vasant Balaji Athavale, M.D. (Paediatrics), D.C.H., F.A.M.S., Vaidyacharya is a renowned paediatrician and an eminent author. He stood first in D.C.H. and in M.D. (Paediatrics). He was the founder of the Paediatric Department of the Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Hospital, Sion established in 1959 and was Head of the Department and Professor of Paediatrics of 30 years form 1959-1990. He was the editor of the Paediatric Clinics of India from 1971 to 1990.he was offered Unicef fellowship in 1965 for his paper read at the ‘International Paediatric Conference’ held in Tokyo. He was the chairman of the worship on ‘Herbal Medicines for Health’ held in Bangkok in 1981.
Dr. Athavale holds the highest degree in Ayurveda, ‘Vaidyacharya’. He has written several books on Ayurveda and has practically updated the entire Ayurveda through his books. These books in English and Marathi are written in a lucid language and shall therefore be useful to Ayurvedic physicians as well as the common man. He was awarded the international award for the ‘Best author of Ayurvedic books’ in 1996. He was honored with a ‘Lifetime Achievement Award’ by the Rashtriya Shikshan Mandal at the international seminar on Ayurveda in 2001.
Dr. Athavale has also written several books for parents which serve as an excellent guide for bringing up children.
Dr. Athavale accords the credit of all his achievements to his parents and teachers.
The second author of this book, Dr. Kamlesh Athavale is the son of Dr. V.B. Athavale. He passed his M.D. (Paediatrics), D.N.B.E. and M.N.A.M.S. with a brilliant academic record. He is a dedicated paediatrician and has completed his fellowship in Neonatology from U.S.A.
He has made significant contributions in writing these books.
According to Ayurveda the liver and the spleen are derived from blood in the foetal life. According to modern medicine, blood is formed by the liver and spleen in early foetal life. This illustrates the close association between blood and the liver since foetal life. Ayurveda refers to only the cells in the blood as blood the plasma the fluid in the blood is included in body fluids.
Ayurveda refers to blood as five thousand years ago, Ayurved mentions that oxygen is carried by blood cells in anaemia when the haemoglobin content in the blood decreases the functions of all the body cells are affected as they do not get adequate oxygen. In India 70% pregnant women and children and 40% adult males duffer from anaemia. This affects their working output and body resistance.
Anaemia is called as panduroga in Ayurveda. The word pandumeans white. In anamia the skin and the mucous membranes called as raktapitta in Ayurveda. The detailed description and treatment of both anaemia and bleeding disorders according to modern medicine as well as Ayurveda are given in this book.
Liver is called yakrut in Ayurveda. Both the words are meaningful. It is said that life depends on the liver. Here the word liver is used with a double meaning that is liver as an anatomical organ of the body and liver which implies one who livers the lifestyle of an individual. The word yakrut is derived from yaha one and krut which literally means does. Thus liver is one which performs important functions of the body.
The book elucidated the functions of the liver and description of jaundice according to modern medicine as well as Ayurveda. In India laymen who are not qualified treatment of jaundice. Patients suffering from jaundice should not take treatment from such people as they are not conversant with the varied causes of jaundice and its complications.
Alcohol is toxic to the liver. Drinking alcohol in excess can give rise to acute alcoholic hepatitis fatty liver alcoholic intoxication and cirrhosis of the liver. Its is difficult to overcome addiction to alcohol as in several cases the fulfils his desire to drink alcohol through the medium of the addict.
The book also describes in detail hepatosplenomegaly cirrhosis of the liver oedema and ascites as per Ayurveda as well modern medicine. The book gives a list of Ayurveda medicines which have proved to be useful in liver disorders by carrying out experiments on animals or clinical trials on patients. The book also gives measures to prevent liver disorders.
This book will prove useful not only to patients with blood and liver disorder but is will also be useful to haematologists gastroenterologists vaidyas doctor medical student and nurses. Every one shall benefit by reading the book in keeping his blood and liver healthy.
| 1 | Blood Ayurvedic concept | |
| 1 | Qualities of blood | 18 |
| 2 | Functions of blood | 18 |
| 3 | Qualities of a person with ideal blood | 19 |
| 4 | Increase in quantity of blood Polycythemia (raktavruddhi) | 19 |
| 5 | Decrease in quantity of blood anaemia (raktakshaya) | 19 |
| 6 | Vitiation of blood (raktadushti) | 20 |
| 7 | Blood Modern concept | 20 |
| 8 | Components of blood | 20 |
| 9 | Sites of blood formation | 21 |
| 10 | Development of blood cells | 21 |
| 2 | Anaemia | |
| 1 | Red blood cells (R..B.C) | 22 |
| 2 | Nutritional and other requirements of red blood cells | 22 |
| 3 | Normal values of haemoglobin and red blood cells In various age groups | 23 |
| 4 | Anaemia | 23 |
| 5 | Causes of anaemia | 23 |
| 6 | Iron deficiency anaemia | 24 |
| 7 | Daily requirement of iron in various age groups | 24 |
| 8 | Iron content in common food items | 25 |
| 9 | why does and infant more than 5 moths old develop anaemia when fed on breast milk alone | 25 |
| 10 | symptoms of anaemia | 25 |
| 11 | Prevention of iron deficiency anaemia | 26 |
| 12 | Ayurvedic medicines containing iron | 26 |
| 13 | Diet rish in iron | 27 |
| 14 | Treatment in anaemia where iron deficiency is not the cause | 27 |
| 15 | Diet beneficial in anaemia according to Ayurvedic concept | 27 |
| 16 | Treatment of anaemia with hepatosplenomegaly | 28 |
| 17 | Spiritual therapy | 28 |
| 18 | Microcytic and megaloblastic anaemia | 29 |
| 19 | Haemolytic anaemia | 30 |
| 20 | Other causes of anamea | 30 |
| 21 | Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia | 32 |
| 22 | Aplastic anaemia | 32 |
| 3 | Leucocytes (white blood cells) | |
| 1 | Types of leucocytes | 35 |
| 2 | Normal values of various types of leucocytes in different age groups | 35 |
| 3 | Neutrophils | 35 |
| 4 | Eosinophils | 36 |
| 5 | Basophils | 36 |
| 6 | Lymphocytes | 36 |
| 7 | Monocytes | 36 |
| 8 | Total white cell count | 36 |
| 9 | Increase in white cell count in pathological conditions | 37 |
| 10 | Eosinophilia | 37 |
| 11 | Lymphocytosis | 37 |
| 12 | Monocytosis | 38 |
| 13 | Neutropenia and agranulocytosis | 38 |
| 4 | Bleeding disorders (raktapitta) Ayurvedic concepts | |
| 1 | Causes | 39 |
| 2 | Types of bleeding disorder | 39 |
| 3 | Symptoms | 39 |
| 4 | Types of bleeding disorder according to the predominnt humour | 40 |
| 5 | Complications of bleeding disorders | 40 |
| 6 | Prognosis of bleeding disorders | 40 |
| 7 | Treatment | 41 |
| 8 | Beneficial diet and other measures | 41 |
| 9 | Medicines usefull in bleeding disorder | 41 |
| 5 | Bleeding disorders (raktapitta) Modern concept | |
| 1 | Blood factors required for blood clotting | 42 |
| 2 | Process of blood clotting | 42 |
| 3 | Epistaxis | 43 |
| 4 | Haemoptysis | 46 |
| 5 | Haematemesis | 47 |
| 6 | Bleeding per rectm | 49 |
| 7 | Haematuria | 50 |
| 8 | Bleeding from the vagina | 51 |
| 9 | Bleeding following increased blood pressure | 51 |
| 10 | Treatment of bleeding according to the increased humour | 52 |
| 11 | Ayurvedic medicines useful to control bleeding | 52 |
| 12 | General treatment in bleeding disorders | 53 |
| 13 | Rasayana treatment for bleeding disorders | 54 |
| 14 | Spiritual therapy | 54 |
| 15 | Diet in bleeding disorders | 55 |
| 6 | Liver (yakrut) | |
| 1 | Life depends on the liver | 58 |
| 2 | Close association of blood and the liver in foetal life | 58 |
| 3 | Functions of the liver | 58 |
| 4 | Why does the tummy of an infant appear bulging | 59 |
| 5 | Why is liver disease commonly suspected in infants and childern | 60 |
| 6 | Causes of liver disorders | 60 |
| 7 | Causes of jaundice Sanskrut references | 61 |
| 7 | Viral hepatitis caused by hepatitis viruses A,B,C,D.and E | |
| 1 | Mode of virus entry | 64 |
| 2 | Infective hepatitis caused by hepatitis A virus | 64 |
| 3 | Infective hepatitis caused by hepatitis ABvirus | 65 |
| 4 | Infective hepatitis caused by hepatitis C virus | 67 |
| 5 | Infective hepatitis caused by hepatitis D virus | 67 |
| 6 | Infective hepatitis caused by hepatitis E virus | 67 |
| 7 | General care of a patient suffering from jaundice | 67 |
| 8 | Jaundice Ayurvedic concept | |
| 1 | Concept of Germs in Ayurveda | 69 |
| 2 | Classification fo Jaundice | 69 |
| 3 | Ruddhapatha kamala | 70 |
| 4 | Koshtha Shakhashirta kamala | 73 |
| 5 | Should one take medication for jaundice from laymen who give free medicines | 15 |
| Sanskrut references | 76 | |
| 9 | Alcohol | |
| 1 | Properties of alcohol | 78 |
| 2 | Constitioun and alcoholic drinks | 78 |
| 3 | Quantity of alcohol | 80 |
| 4 | Alcohol and seasons | 80 |
| 5 | How should one drink alcohol | 80 |
| 6 | Contraindications for drinking alcohol | 81 |
| 7 | How to overcome addiction to alcohol | 81 |
| Sanskrut references | 82 | |
| 10 | Diseases caused by excessive consumption or alcohol for a prolonged period | |
| 1 | Alcohol is toxic to the liver | 87 |
| 2 | Pathogenesis | 87 |
| 3 | Acute aloholic hepatitis | 87 |
| 4 | Fatty liver | 88 |
| 5 | Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver | 88 |
| 6 | Madayaya | 88 |
| 7 | Why is it difficult to get rid of addiction to alcohol | 89 |
| Sanskrut references | 90 | |
| 11 | Hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen) | |
| 1 | Causes of enlargement of the liver and spleen | 91 |
| 2 | General Ayurvedic treatment | 91 |
| 3 | Rasayana medicines | 93 |
| 4 | Rasayana medicines | 93 |
| 5 | Spiritual therapy (karma vipak) | 94 |
| Sanskrut references | 95 | |
| 12 | Cirrhosis of the liver (yakrutodara) | |
| 1 | Causes of cirrhosis | 97 |
| 2 | Symptoms | 97 |
| 3 | Diet according to modern medicine | 98 |
| 4 | Hepatic coma | 99 |
| 5 | Liver transplant | 99 |
| 6 | Ayurvedic treatment | 100 |
| 13 | Oedema (shotha) | |
| 1 | Causes of localised swelling | 101 |
| 2 | Causes of generalised swelling all over the body | 101 |
| 3 | Pathogenesis | 102 |
| 4 | Premonitory symptoms | 103 |
| 5 | Ama stage of oedema | 103 |
| 6 | Symptoms | 103 |
| 7 | Complication of oedema | 104 |
| 8 | Prognosis | 104 |
| 9 | Principles of treatment | 105 |
| 10 | Treatment during the ama stage | 105 |
| 11 | Treatment during the nirama stage | 106 |
| 12 | Diet in the ama stage | 106 |
| 13 | Diet in the nirama stage | 107 |
| 14 | Classification of oedema according to the predominant humour | 107 |
| 15 | vataja oedema | 107 |
| 16 | Pitaja oedema | 108 |
| 17 | Kaphaja oedema | 109 |
| 18 | Vatapittaja oedema | 110 |
| 19 | Kaphavataja oedema | 110 |
| 20 | Tridoshaja oedema | 111 |
| 21 | Diet in oedema | 113 |
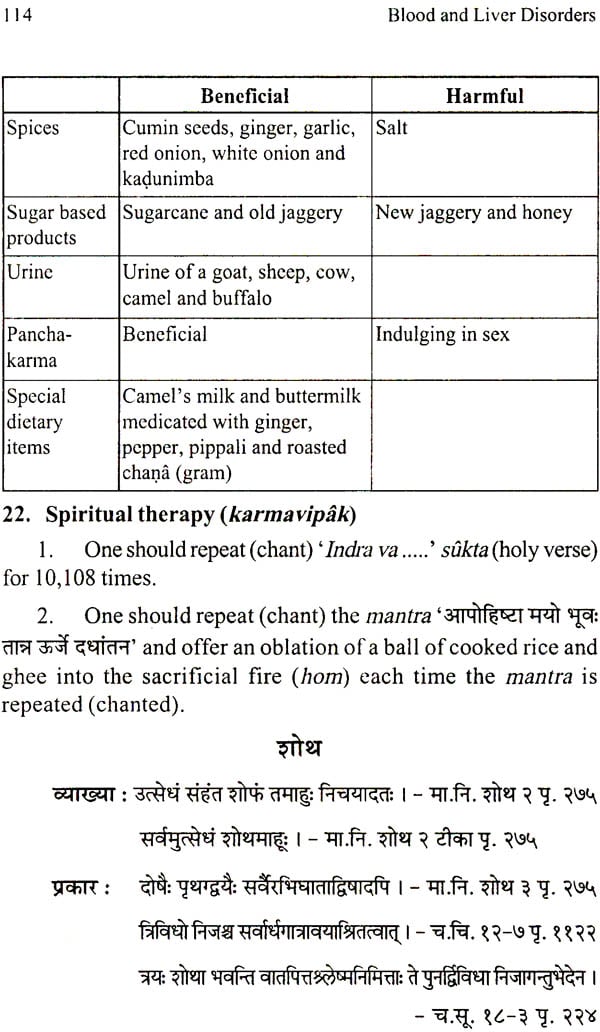
| 22 | Spiritual therapy (karma vipak) | 114 |
| Sanskrut references | 114 | |
| 14 | Ascites (Jalodara) | |
| 1 | Causes of ascites | 120 |
| 2 | Classifications of udara | 120 |
| 3 | General treatmetn of ascites | 121 |
| 4 | Diet in ascites | 123 |
| 5 | Spiritual theraphy | 124 |
| Sanskrut references | 124 | |
| 15 | Drugs useful in liver disorders | |
| 1 | Best medicine in diseases of blood and liver | 134 |
| 2 | Prevention of liver disorders | 137 |
| 16 | Preparation of Ayurvedic recipes Bibliography | 160 |